Section: New Results
Scenario Recognition with depth camera
Participants : Bernard Boulay, Daniel Zullo, Swaminathan Sankaranarayanan, François Brémond.
Thanks to Microsoft and its kinect sensor, RGB-depth camera becomes popular and accessible. The basic idea of depth camera is to combine a visible camera, with an IR camera associated to a laser to determine the depth of each image pixel. This kind of sensor is well adapted for applications which monitor people (e.g. monitoring Alzeihmer patient in hospital): because the people are in a predefined area and near the camera.
The depth cameras have two main advantages: first, the output image contains depth information and second, the sensor is independent from the light changes (IR sensor).
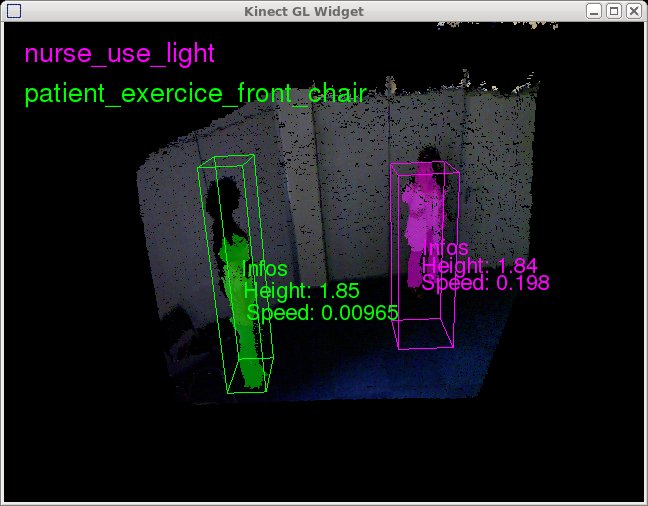
In our work, we propose to use the kinect sensor to acquire 3D images, detect the people and recognize interesting activities (see Figure 21 ).
|
The nestk library is used to manage the kinect sensor. This library is based on OpenNI framework (an open source driver) to acquire the images. Moreover the library is able to compute some treatments (e.g. people detection) and to provide a true 3D map of the scene in the referential of the kinect.
Basic attributes are computed for each detected person: 3D position, 3D height,... These attributes are then used to compute more complex information: speed, global posture to recognize interesting activities thanks to the ScreKs framework (scenario recognition based on expert knowledge) of the SUP platform as walking, stopping, standing, sitting,... (following a protocol delivered by doctors). Then we have a plug and play system able to recognize basic activities associated to a person.
Moreover, if information on the scene, as interesting zones, or equipment are available, complex activities can be recognized as nurse explaining exercise or nurse switching off the light.
The next step, is to use the human skeleton detection to recognize precisely the posture of the patient in order to understand more precise activities and infer a behaviour model.