Keywords
Computer Science and Digital Science
- A1.3.2. Mobile distributed systems
- A1.5.2. Communicating systems
- A2.3.1. Embedded systems
- A3.4.1. Supervised learning
- A3.4.2. Unsupervised learning
- A3.4.3. Reinforcement learning
- A3.4.4. Optimization and learning
- A3.4.5. Bayesian methods
- A3.4.6. Neural networks
- A3.4.8. Deep learning
- A5.1. Human-Computer Interaction
- A5.4.1. Object recognition
- A5.4.2. Activity recognition
- A5.4.4. 3D and spatio-temporal reconstruction
- A5.4.5. Object tracking and motion analysis
- A5.4.6. Object localization
- A5.4.7. Visual servoing
- A5.10.2. Perception
- A5.10.3. Planning
- A5.10.4. Robot control
- A5.10.5. Robot interaction (with the environment, humans, other robots)
- A5.10.6. Swarm robotics
- A5.10.7. Learning
- A5.11.1. Human activity analysis and recognition
- A6.1.2. Stochastic Modeling
- A6.1.3. Discrete Modeling (multi-agent, people centered)
- A6.2.3. Probabilistic methods
- A6.2.6. Optimization
- A6.4.1. Deterministic control
- A6.4.2. Stochastic control
- A6.4.3. Observability and Controlability
- A8.2. Optimization
- A8.2.1. Operations research
- A8.2.2. Evolutionary algorithms
- A8.11. Game Theory
- A9.2. Machine learning
- A9.5. Robotics
- A9.6. Decision support
- A9.7. AI algorithmics
- A9.9. Distributed AI, Multi-agent
- A9.10. Hybrid approaches for AI
Other Research Topics and Application Domains
- B5.2.1. Road vehicles
- B5.6. Robotic systems
- B7.1.2. Road traffic
- B8.4. Security and personal assistance
1 Team members, visitors, external collaborators
Research Scientists
- Christian Laugier [INRIA, Emeritus, HDR]
- Agostino Martinelli [INRIA, Researcher]
- Alessandro Renzaglia [INRIA, Researcher]
- David Sierra Gonzalez [INRIA, Starting Research Position]
Faculty Members
- Olivier Simonin [Team leader, INSA LYON, Professor, HDR]
- Jilles Dibangoye [INSA LYON, Associate Professor]
- Christine Solnon [INSA LYON, Professor, HDR]
- Anne Spalanzani [UGA, Professor, HDR]
Post-Doctoral Fellows
- Wenqian Liu [INRIA]
- LoÏc Rouquette [CNRS, from Oct 2022]
PhD Students
- Rabbia Asghar [INRIA]
- Théotime Balaguer [INSA LYON, from Nov 2022]
- Edward Beeching [INRIA]
- Alexandre Bonnefond [INRIA]
- Estéban Carvalho [UGA]
- Aurélien Delage [INSA LYON]
- Niranjan Deshpande [INRIA, ANR grant]
- Manuel Diaz Zapata [INRIA]
- Romain Fontaine [INSA LYON]
- Jean-Baptiste Horel [INRIA]
- Pierre Marza [INSA Lyon]
- Xiao Peng [INSAVALOR]
- Benoit Renault [CPE LYON / INSAVALOR]
- LoÏc Rouquette [CNRS, until Nov 2022]
- Samuele Zoboli [INSA LYON]
Technical Staff
- Andres Gonzalez Moreno [INRIA]
- Robin Baruffa [INRIA, Engineer, from Oct 2022]
- Johan Faure [INRIA, Engineer, from Mar 2022]
- Simon Ferrier [INSAVALOR, from Sep 2022]
- Thomas Genevois [INRIA, Engineer]
- Pierrick Koch [INRIA, Engineer, from Mar 2022]
- Khushdeep Singh Mann [INRIA, Engineer]
- Anshul Paigwar [INRIA, until Jul 2022]
- Lukas Rummelhard [INRIA, SED Inria Grenoble]
- Gustavo Andres Salazar Gomez [INRIA, Engineer, from Sep 2022, INRIA]
- Amrita Suresh [INRIA, until Jul 2022]
- Abhishek Tomy [INRIA, Engineer]
- Stéphane d'Alu [INSA LYON, Engineer]
Interns and Apprentices
- Samir Abou Haidar [INRIA, from Feb 2022 until Jun 2022]
- Marco Ambrogi [INSAVALOR, from Sep 2022]
- Olivier Idir [INSA Lyon (CITI), from Feb 2022 until Jul 2022]
- Gustavo Andres Salazar Gomez [INRIA, from Mar 2022 until Aug 2022]
Administrative Assistant
- Anouchka Ronceray [INRIA]
External Collaborators
- Ozgur Erkent [UNIV HACETTEPE]
- Fabrice Jumel [CPE LYON]
- Jacques Saraydaryan [CPE LYON]
2 Overall objectives
2.1 Origin of the project
Chroma is a bi-localized project-team at Inria Lyon and Inria Grenoble (in Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region). The project was launched in 2015 before it became officially an Inria project-team on December 1st, 2017. It brings together experts in perception and decision-making for mobile robotics and intelligent transport, all of them sharing common approaches that mainly relate to the field of Artificial Intelligence. It was originally founded by members of the working group on robotics at CITI lab1, led by Prof. Olivier Simonin (INSA Lyon2), and members from Inria project-team eMotion (2002-2014), led by Christian Laugier, at Inria Grenoble. Earlier members include Olivier Simonin (Prof. INSA Lyon), Christian Laugier (Inria researcher DR, Grenoble), Anne Spalanzani (Prof., UGA), Jilles Dibangoye (Asso. Prof. INSA Lyon) and Agostino Martinelli (Inria researcher CR, Grenoble). On January 2020, Christine Solnon (Prof. INSA Lyon) joined the team, thanks to her transfer from LIRIS lab. to CITI lab. On October 2021, Alessandro Renzaglia (Inria researcher CR, Lyon) was recruited through the Inria researcher recruitment campaign.
The overall objective of Chroma is to address fundamental and open issues that lie at the intersection of the emerging research fields called “Human Centered Robotics” 3, “Multi-Robot Systems" 4, and AI for humanity.
More precisely, our goal is to design algorithms and models that allow autonomous agents to perceive, decide, learn, and finally adapt to their environment. A focus is given to unknown and human-populated environments, where robots or vehicles have to navigate and cooperate to fulfill complex tasks.
In this context, recent advances in embedded computational power, sensor and communication technologies, and miniaturized mechatronic systems, make the required technological breakthroughs possible.
Chroma is clearly positioned in the "Artificial Intelligence and Autonomous systems" research theme of the Inria 2018-2022 Strategic Plan. More specifically we refer to the "Augmented Intelligence" challenge (connected autonomous vehicles) and to the "Human centred digital world" challenge (interactive adaptation).
2.2 Research themes
To address the mentioned challenges, we take advantage of recent advances in: probabilistic methods, machine learning, planning techniques, multi-agent decision making, and constrained optimisation tools. We also draw inspiration from other disciplines such as Sociology, to take into account human models, or Physics/Biology, to study self-organized systems.
Chroma research is organized in two main axes : i) Perception and Situation Awareness ii) Decision Making. Next, we elaborate more about these axes.
-
Perception and Situation Awareness.
This theme aims at understanding complex dynamic scenes, involving mobile objects and human beings, by exploiting prior knowledge and streams of perceptual data coming from various sensors.
To this end, we investigate three complementary research problems:
- Bayesian & AI based Perception: How to interpret in real-time a complex dynamic scene perceived using a set of different sensors, and how to predict the near future evolution of this dynamic scene and the related collision risks ? How to extract the semantic information and to process it for the autonomous navigation step.
- Modeling and simulation of dynamic environments: How to model or learn the behavior of dynamic agents (pedestrians, cars, cyclists...) in order to better anticipate their trajectories?
- Robust state estimation: Acquire a deep understanding on several sensor fusion problems and investigate their observability properties in the case of unknown inputs.
-
Decision making.
This theme aims to design algorithms and architectures that can achieve both scalability and quality for decision making in intelligent robotic systems and more generally for problem solving.
Our methodology builds upon advantages of three (complementary) approaches: online planning, machine learning, and NP-hard optimization problem solving.
- Online planning: In this theme we study planning algorithms for single and fleet of cooperative mobile robots when they face complex and dynamics environments, i.e. populated by humans and/or mostly unknown.
- Machine learning: We search for structural properties–e.g., uniform continuity–which enable us to design efficient planning and (deep) reinforcement learning methods to solving complex single or multi-agent decision-making tasks.
- Offline constrained optimisation problem: We design and study approaches based on Constraint Programming (CP) and meta-heuristics to solve NP-hard problems such as planning and routing problems, for example.
Chroma is also concerned with applications and transfer of the scientific results. Our main applications include autonomous and connected vehicles, service robotics, exploration & mapping tasks with ground and aerial robots. Chroma is currently involved in several projects in collaboration with automobile companies (Renault, Toyota) and some startups (see Section 4).
The team has its own robotic platforms to support the experimentation activity (see5). In Grenoble, we have two experimental vehicles equipped with various sensors: a Toyota Lexus and a Renault Zoe; the Zoe car has been automated in December 2016. We have also developed two experimental test tracks respectively at Inria Grenoble (including connected roadside sensors and a controlled dummy pedestrian) and at IRT Nanoelec & CEA Grenoble (including a road intersection with traffic lights and several urban road equipments). In Lyon, we have a fleet of UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles) composed of 4 PX4 Vision, 2 IntelAero and 5 mini-UAVs Crazyflies. We have also a fleet of ground robots composed of 16 Turtlebot and 3 humanoids Pepper. The platforms are maintained and developed by contractual engineers, and by Lukas Rummelhard, from SED, in Grenoble.
3 Research program
3.1 Introduction
The Chroma team aims to deal with different issues of autonomous navigation and intelligent transport: perception, decision-making and cooperation. Figure 1 schemes the different themes and sub-themes investigated by Chroma.
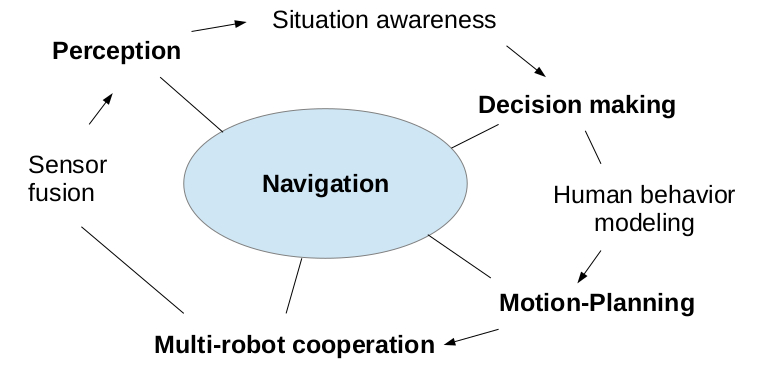
Research themes of the team: Sensor fusion, perception, situation awareness, decision making, motion planning, multi-robot cooperation
We present here after our approaches to address these different themes of research, and how they combine altogether to contribute to the general problem of robot navigation. Chroma pays particular attention to the problem of autonomous navigation in highly dynamic environments populated by humans and cooperation in multi-robot systems. We share this goal with other major robotic laboratories/teams in the world, such as Autonomous Systems Lab at ETH Zurich, Robotic Embedded Systems Laboratory at USC, KIT 6 (Prof. Christoph Stiller lab and Prof. Ruediger Dillmann lab), UC Berkeley, Vislab Parma (Prof. Alberto Broggi), and iCeiRA 7 laboratory in Taipei, to cite a few. Chroma collaborates at various levels (visits, postdocs, research projects, common publications, etc.) with most of these laboratories.
3.2 Perception and Situation Awareness
Project-team positioning
The team carries out research across the full (software) stack of an autonomous driving system. This goes from perception of the environment to motion forecasting and trajectory optimization. While most of the techniques that we develop can stand on their own and are typically tested on our experimental platforms, we slowly move towards their complete integration. This will result in a functioning autonomous driving software stack. Beyond that point, we envision to focus our research on developing new methods that improve the individual performance of each of the stack’s components, as well as the global performance. This is alike to how autonomous driving companies operate (e.g. Waymo, Cruise, Tesla). The research topics that we explore are addressed by a very long list of international research laboratories and private companies. However, in terms of scope, we find the research groups of Prof. Dr.-Ing. Christoph Stiller (KIT), Prof. Marcelo Ang (NUS), Prof. Daniela Rus (MIT) and Prof. Wolfram Burgard (TRI California) to be the closest to us; we have active interconnections with these research groups (e.g. in the scope of the IEEE RAS Technical Committee AGV-ITS we are co-chairing any of the related annual Workshops). At the national level, we are cooperating in the framework of several R&D projects with UTC, Institut Pascal Clermont-Ferrand, University Gustave Eiffel, and the Inria Teams RITS, Acentauri and Convecs. Our main research originality relies in the combination of Bayesian approaches, AI technologies, Human-Vehicle interactions models, Robust State Estimation formalism, and a mix of Real experiments and Formal methods for validating our technologies in complex real world dynamic scenarios.
Our research on visual-inertial sensor fusion is closely related to the research carried out by the group of Prof. Stergios Roumeliotis (University of Minnesota) and the group of Prof. Davide Scaramuzza (University of Zurich). Our originality in this context is the introduction of closed-form solutions instead of filter-based approaches.
Scientific achievements
1. Bayesian & AI based Environment Perception and Forecasting
In order to be able to operate in a dynamic environment surrounded by humans or other robots, an autonomous system needs to Perceive, Understand and Forecast any changes of its surroundings. We have investigated the perception task from different angles, most of them with the shared nexus of involving both Bayesian approaches and Deep Learning models.
Bayesian Perception: The team's work on Bayesian approaches has given rise over the last decade to numerous publications and to some patents and licensed software8. Over the past 4 years, we have focused on collision risk assessment, safe navigation and semantic processing issues, with a strong emphasis on the integration and the validation of our technologies on real-time experimental platforms. The new results gave rise to the filing of two patents and to a transfer of technology with a French SME and with a Japanese international company (R&D work still ongoing). The main advances relate to (1) the generalization of the principle of Bayesian fusion in order to be able to integrate connected sensors located outside the ego-vehicle (infrastructure or other vehicles), (2) new real-time methods allowing to better estimate the risks of collision and make navigation safer (including path planning), and (3) experimental validation principle combining real tests, synchronized simulated environments (augmented reality principle) and formal methods 49, 86, 93, 48. A new PhD thesis addressing the subject of validating AI-based perception components in autonomous vehicles, with a particular focus on formal validation methods, has started in 2021 in cooperation with the Inria Convecs team (funding: French project PRISSMA).
Situation awareness & Environment Forecasting: In addition to the above-mentioned work, we have developed AI-based methods for extracting the semantic information of observed scenes 83, 80, 84, 111. In particular, we have developed hybrid methods for 3D object detection 95, 11496, semantic mapping of the environment from a top-view 67, 68, 69 and ground plane estimation and segmentation 94. We have likewise investigated the use of domain adaptation techniques to mitigate the degradation of some of the previous algorithms across different weather conditions 65, 62 and sensor modalities 111. In terms of environment forecasting, two PhD theses were dedicated to the task of predicting the future behavior of surrounding traffic 47, 115. The first of them targeted road intersections; the second focused on highway scenarios and leveraged a behavioral model learned from driving demonstrations 112 to cope with the long-term prediction horizon necessary for highways. Both theses also explored how to integrate the forecasting models into a behavioral planning framework 113. In addition to these forecasting models, we have also carried out research on localization 46, tracking 66, detection of abnormal behaviors 122, and contextualization of complex risk mitigation scenarios 110. A new PhD thesis addressing the subject of “Hybrid Sensor fusion” was launched in 2021 (funding: EU CPS4EU).
2. Modeling and simulation of dynamic environments
Modeling pedestrian's behaviors with a limited amount of data is a challenge. In Pavan Vasishta's PhD and the ANR Valet project, we proposed to learn typical pedestrian behavior using HMM, starting from prior knowledge itself derived from the JJ Gibson’s sociological principles of “Natural Vision” and “Natural Movement”. The work assumes that there are some parts of the observed scene which are more attractive to pedestrians and some areas, repulsive 118.
Pedestrians simulation. We studied the behavior of pedestrians in a shared space with an autonomous vehicle by modeling and simulating realistic pedestrian behavior. Our approach integrates empirical observations and concepts from social science into an agent-based model and simulator for an application in robotics. At each step, the proposed model has been evaluated and validated through simulations of many scenarios and comparisons with real-world data. Then we proposed the simulator SPACiSS, "Simulator for Pedestrians and an Autonomous Car in Shared Spaces", an open source simulator based on the PedSim framework that can simulate interactions between pedestrians and vehicles in different shared space scenarios. With the integration in the ROS framework, commonly used in robotics, the software is designed as an environment to test autonomous navigation systems 98, 99100, 101.
Robots in human flows. Another work, led by J. Saraydaryan, was conduced on simulating pedestrians and mobile robots in indoor environments, by extending PedSim. This work aimed to simulated scenarios where robots perceive and map human flows and compute paths by exploiting such information (in the cost-function of A* algorithm) 10874.
3. Robust State Estimation
Our investigations have been in the framework of the unknown input observability problem. This problem was introduced and firstly investigated during the sixties and has remained unsolved for 50 years. During the last 8 years, we have studied this fundamental open problem. Due to its complexity, the general solution was published in a book 89. The main result of this year is the extension of the above solution. Specifically, in 89, we provided the solution by restricting our investigation to systems that satisfy a special assumption that is called canonicity with respect to the unknown inputs. In 2022, after an exhaustive characterization of the concept of canonicity, we also accounted for the case when this assumption is not satisfied and we obtained the most general solution of the problem. These results have been published by the Journal of Information Fusion 13. A further result obtained in 2022, is the extension of the well known observability rank condition to time-varying systems. This extension has been published by the Transaction on Automatic Control 12.
Collaborations
- Main long-term industrial collaborations: IRT Nanoelec & CEA 10 years), Toyota Motor Europe (12 years, R&D center Zaventen-Brussels), Renault (10 years), SME Easymile (3 years), Sumitomo Japan (started in 2019), Iveco (3 years in the framework of STAR project). These collaborations are funded either by Industry or by National, Regional or European projects. The main outputs are common publications, softwares development, patents or technological transfers. Two former doctoral students of our team were recruited some years ago by respectively TME Zaventen and Renault R&D centers.
- Main academic collaborations: Institut Pascal Clermont-Ferrand, University Compiegne (UTC), University Gustave Eiffel, several Inria Teams (RITS, Acentauri, Convecs, Rainbow). These collaborations are most of the time conducted in the scope of various National R&D projects (FUI, PIA, ANR, etc.). The main outputs are scientific and software exchanges. In addition, we had a fruitful collaboration with B. Mourrain from the Inria-Aromath team. The goal was to find the analytical solution of a polynomial equation system that fully characterizes the cooperative visual-inertial sensor fusion problem with 2 agents.
- International cooperation for scientific exchanges and IEEE scientific events organization, e.g. NUS & NTU Singapore, Peking University, TRI Mountain View, KIT Karlsruhe, Coimbra University. We have constantly interacted with Prof. D. Scaramuzza from the university of Zurich to make our findings in visual inertial sensor fusion more usable in a realistic context (e.g., for the autonomous navigation of drones).
3.3 Decision Making
Project-team positioning
In his reference book Planning algorithms78, S. LaValle discusses the different dimensions that make the motion-planning a complex problem, which are the number of robots, the obstacle regions, the uncertainty of perception and action, and the allowable velocities. In particular, it is emphasized that multiple robot planning in complex environments are NP-hard problems which implies that exact approaches have exponential time complexities in the worst case (unless P=NP). Moreover, dynamic and uncertain environments, as human-populated ones, expand this complexity. In this context, we aim at scaling up decision-making in human-populated environments and in multi-robot systems, while dealing with the intrinsic limits of the robots and machines (computation capacity, limited communication). To address these challenges, we explore new algorithms and AI architectures following three directions: online (or real-time) planning, machine learning to adapt to the complexity of uncertain environments, and combinatorial optimization to deal with offline constrained problems. Combining these approaches, seeking to scale up them, and also evaluating them with real platforms are also elements of originality of our work.
We share these goals with other laboratories/teams in the world, such as the Mobile Robotics Laboratory and Intelligent Systems "IntRoLab" at Sherbrooke University (Montreal) led by Prof. F. Michaud, the Learning Agents Research Group (LARG) within the AI Lab at the University of Texas (Austin) led by Prof. P. Stone, the Autonomous Systems Lab at ETH Zurich (Switzerland) led by R. Siegwart, the Robotic Sensor Networks Lab at the University of Minnesota (USA) led by Prof. V. Isler, and the Autonomous Robots Lab at NTNU (Norway) to cite a few. At Inria, we share some of the objectives with the LARSEN team in Nancy (multi-agent machine learning, multi-robot planning) and the RAINBOW team in Rennes (multi-UAV planning). We have also collaborations with the ACENTAURY team, in Sophia Antipolis, about autonomous navigation among humans. In France, among other labs involved on similar subjects, we can cite the LAAS (CNRS, Toulouse), the ISIR lab (CNRS, Paris Sorbonne Univ.) and the MAD team in Caen University. In the more generic domain of problem solving, we can mention the TASC team at LS2N (Nantes), the CRIL lab (Lens) and, at the international level, we can cite the Insight Centre for Data Analytics (Cork, Ireland).
Scientific achievements
1. Online Planning
In this theme, we address online planning when robots/vehicles/UAVs have to navigate or work in complex and generally unknown environments. The challenge comes from the necessity for entities to decide actions in real time and with limited information. Hereafter we present our main results following different problem contexts.
Social and ethic navigation
We investigated new methods to build safe and socially compliant trajectories among humans using models of behaviors presented in Axis I. A focus on navigation of an autonomous vehicle among crowds has been done were there is no free space to plan a safe trajectory (M. Kabtoul's PhD, ANR Hianic Project). We proposed a solution that is a proactive social navigation framework. The system is based on the idea of the coupled navigation behavior between the pedestrian and the vehicle in shared spaces. The system takes into account the cooperative nature of human behavior and exploits it to explore new navigation options, and navigate the shared space “proactively" 76, 75. We obtained promising results using the SPACISS simulator previously described. We also investigated ethic navigation when an autonomous vehicle cannot avoid a collision with an object or a vulnerable road user (L. Serafim Guardini's PhD). We exploit accidentology data where each class of object or agent presents an injury probability with respect to the impact speed and ethical/economical/political factors. Our method generates a cost map containing a collision probability along with its associated risk of injury, which are used to plan trajectories with the lowest risk 110.
We also investigated another navigation problem, which is NAMO (Navigation Among Movable Obstacles). We extended NAMO in two directions considering social constraints when robots move obstacles (B. Renault's PhD). First, we examined where obstacles should be optimally moved with regards to space access (called Social-NAMO). We derived new spatial cost functions and NAMO algorithms preserving accesses 102. Second, we generalized the problem to robots (called MR-NAMO). We proposed a local coordination strategy exploiting Social-NAMO rearrangement properties and offering online efficient plans (under review). For evaluation, we developped a simulator (S-NAMO-SIM) that we share with the communauty.
Multi-robot exploration
An important part of our research is focused on designing new online planning solutions for multi-robot systems to accomplish exploration and observation gathering tasks in complex and dynamic environments. Problems related to computational and communication constraints are here crucial, and distributed approaches are fundamental to overcome them and obtain robust solutions.
Following these goals, a particular attention has been given to the exploration/mapping of 3D environments with a team of aerial vehicles, for which we presented a new decentralized solution based on the combination of a stochastic optimization approach with a more classic strategy that exploits frontier points 105. In 104, we then showed how this approach is part of a more general formulation that can deal with the optimal deployment coverage as well, for which we also studied the impact of an offline initialization step based on very partial information on the environment. Stochastic-based planning methods have been also exploited to propose a new source seeking strategy 103. This solution is based on robust estimations of the signal gradient obtained by the robots while exploring the environment in predefined symmetric formations 56 and that are then used to bias a correlated random walk that guides the robots.
Connected to this subject, we also investigated multi-robot strategies to cover complex scenes/ environments, by introducing multi-resolution maps. This concerned human activity observation by a set of ground robots (90) and more recently inspection of large structures with aerial robots (in the framework of the European project BugWright2, in collaboration with LSL, Austria).
Swarm navigation
In the context of self-reorganized systems, or swarm robotics, we explore how collective navigation can be defined and adapted to fleets of communicating robots. In A. Bonnefond's PhD, we studied flocking models, where each agent communicates locally its speed and position, and by simulating radio propagation we examined how obstacles impact the flocking robustness. Then we extended and combined two standard models, Olfati-Saber and Vásárhelyi, to improve their ability to stay connected while evolving in environments with different obstacle distributions 54. This work is supported by the Inria/DGA Dynaflock project and by the national Equipex+ TIRREX infrastructure. Related to this work, we address Controled Mobility where navigation must take into account the need of maintaining the fleet connectivity. In R. Grunblatt's PhD, we proposed a distributed algorithm that optimizes communication in a swarm of UAVs by changing their antenna orientation online 11. This work is continued in the ANR CONCERTO project.
2. Machine Learning
Machine learning techniques for decision-making are autonomous algorithms for computing behaviors, also called policies or strategies, which describe what action an agent should take when at a given state. Learning to act in complex environments requires knowledge about the structure of underlying decision-making problems. We contribute in revealing insightful underlying structures, exploiting them within existing or customized algorithms, and showing they improve performances in a wide variety of decision-making problems. For instance, optimal policies may have concise representations of their mental states, e.g., sufficient statistics, ego-centric neural-network architectures.
In the context of POMDPs9, dec-POMDPs, zs-POSGs10, and st-POSGs, we have identified a unified framework for solving these problems 64. Our methodological framework splits into five steps. First, we have shown that all these problems are convertible into a single problem called a common-knowledge game 64. Then, we recast the (possibly discrete) problem into a continuous one. Furthermore, we establish uniform continuity properties for general and hierarchical dec-POMDPs. We proved that optimal value functions for general and hierarchical dec-POMDPs are PWLC 64, 121. We also established optimal value functions for general zs-POSGs that are Lipschitz continuous 57, 58. Finally, we designed planning algorithms for games against Nature 70, pure competitive games 59, as well as for pure cooperative games 64. We extended exact and deep reinforcement learning algorithms for general dec-POMDPs 64. We finally conducted applications of deep reinforcement along two main directions: autonomous transportation systems 55; and automatic control systems 123.
Creating agents capable of high-level reasoning based on structured memory was the main topic of C. Wolf during its Inria "delegation" in Chroma (2017-19). In the PhD thesis of E. Beeching we proposed EgoMap, a spatially structured metric neural memory architecture in deep reinforcement learning. Through visualizations, the agent learns to map relevant objects in its spatial memory without any supervision purely from reward, see 52 (ICPR), 51 (ECCV) and 50 (ECML). In late 2019, C. Wolf obtained the AI Chair "REMEMBER", involving O. Simonin and J. Dibangoye from Chroma and L. Matignon from LIRIS lab/Univ Lyon 1. In this context, the PhD of P. Marza proposes to use an implicit representation of the environment to navigate towards targets. Neural fields are a recent category of approaches where the geometry, and eventually the semantics, of a 3D scene are encapsulated into the weights of a trained neural network.
As mentioned in Axis I, making appropriate decisions for safe robot / vehicle navigation is highly dependent on the results of the perception step. Indeed, the critical elements of a complex dynamic scene must first be extracted, classified and tracked in real time, by combining Bayesian and AI approaches to build "semantic grids" 8285, 67, 65. Two types of decision-making based on RL were developed for autonomous driving on highways and road junctions respectively, as part of the doctoral theses of David Sierra-Gonzalez 115 and Mathieu Barbier 47.
A last activity concerns our involvement in the RoboCup11 competition. In 2017 we founded the LyonTech team12 to participate to the RoboCup@Home challenge within the Pepper league. We worked on learning and integrating high-level functionalities such as object and people recognition, mapping and planning in indoor environments (see 73). We reached the 5th place in 2018, the 3rd place in 2019, the 2d place in 2021, and awarded the best scientific paper at the RoboCup conference in 2019 109.
3. Offline constrained optimisation problems
In this theme, we study and design algorithms for solving NP-hard constrained optimization problems (COPs) such as vehicle routing problems, or multi-agent path finding problems. We more particularly study approaches based on Constraint Programming (CP), that provides declarative languages for describing these problems by means of constraints, and generic algorithms for solving them by means of constraint propagation.
In the context of the European project BugWright2 and the PhD thesis of Xiao Peng (started in Nov. 2020), we study a new multi-agent path finding problem for tethered robots, that are attached with cables to anchor points. In 97, we show how to compute bounds for this problem by solving well known assignment problems, and we introduce a CP model for solving the problem to optimality. In 92, we extend this approach to the case of non point-sized robots.
In the context of the PhD thesis of Romain Fontaine (started in Oct. 2020), we study vehicle routing problems with time-dependent cost functions (such that travel times between locations to visit may change along the day), and we design new solving approaches based on an anytime extension of A* 71, 41. We study the impact of time-window constraints on the satisfiability and the difficulty of routing problems in 106.
Besides planning and routing problems which are at the core of Chroma topics, we also investigate the interest of using CP solvers for solving cryptanalysis problems 26.
Collaborations
- Social navigation: collaboration with Julie Dugdale and Dominique Vaufreydaz, Asso. Prof. at LIG Laboratory and with Prof. Philippe Martinet from Acentori Inria team (common PhD students and projects: ANR VALET and ANR HIANIC).
- Multi-robot exploration: Prof. Cedric Pradalier from GeorgiaTech Metz/CNRS (France) leading the European project BugWright2 — Prof. Luca Schenato from University of Padova (Italy).
- Swarm of UAVs: Prof. Isabelle Guérin-Lassous from LIP lab/Inria DANTE team (common PhD students and projects: ANR CONCERTO, INRIA/DGA DynaFlock) — Research Director Isabelle Fantoni from CNRS/LS2N Lab in Nantes (common projects: ANR CONCERTO, Equipex TIRREX) — Dr. Melanie Schranz, senior researcher at LakeSide Lab, Austria (BugWright2 project).
- Machine Learning: strong collaborations with Christian Wolf, Naver Labs Europe & LIRIS lab/INSA13 (common PhD students and projects: ANR DELICIO, ANR AI Chair REMEMBER) and with Laetitia Matignon, Asso. Prof. at LIRIS lab/Univ Lyon 1 (common projects and Phd/Master students) — Akshat Kumar, Asso. Prof. at School of Computing and Information Systems (Singapore) — Abdallah Saffidine, Research Asso. at University of New South Wales (Sydney) — Prof. Stéphane Canu at INSA Rouen — Olivier Buffet, Vincent Thomas and François Charpillet, Inria researchers in LARSEN team, Nancy (common publications and project ANR PLASMA).
- Semantic grids for autonomous navigation: Collaboration with Toyota Motor Europe (TME), R&D center Zaventen (Brussels). R&D contracts, common publications and patents.
- Constrained optimization: Omar Rifki (Post-doc) and Thierry Garaix (Ass. Prof) at LIMOS Ecole des Mines de Saint Etienne — Pascal Lafourcade and François Delobel, Asso. Prof. at LIMOS Université Clermont-Ferrand.
4 Application domains
4.1 Introduction
Applications in Chroma are organized in two main domains : i) Future cars and transportation of persons and goods in cities, ii) Service robotics with ground and aerial robots. These domains correspond to the experimental fields initiated in Grenoble (eMotion team) and in Lyon (CITI lab). However, the scientific objectives described in the previous sections are intended to apply equally to these applicative domains. Even if our work on Bayesian Perception is today applied to the intelligent vehicle domain, we aim to generalize to any mobile robots. The same remark applies to the work on multi-agent decision making. We aim to apply algorithms to any fleet of mobile robots (service robots, connected vehicles, UAVs). This is the philosophy of the team since its creation.




4.2 Future cars and transportation systems
Thanks to the introduction of new sensor and ICT technologies in cars and in mass transportation systems, and also to the pressure of economical and security requirements of our modern society, this application domain is quickly changing. Various technologies are currently developed by both research and industrial laboratories. These technologies are progressively arriving at maturity, as it is witnessed by the results of large scale experiments and challenges such as the Google’s car project and several future products announcements made by the car industry. Moreover, the legal issue starts to be addressed in USA (see for instance the recent laws in Nevada and in California authorizing autonomous vehicles on roads) and in several other countries (including France).
In this context, we are interested in the development of ADAS 14 systems aimed at improving comfort and safety of the cars users (e.g., ACC, emergency braking, danger warnings), of Fully Autonomous Driving functions for controlling the displacements of private or public vehicles in some particular driving situations and/or in some equipped areas (e.g., automated car parks or captive fleets in downtown centers or private sites), and of Intelligent Transport including optimization of existing transportation solutions.
Since about 8 years, we are collaborating with Toyota and with Renault-Nissan on these applications (bilateral contracts, PhD Theses, shared patents), but also recently with Volvo group (2016-20). We are also strongly involved (since 2012) in the innovation project Perfect then now Security for autonomous vehicle of the IRT 15 Nanoelec (transportation domain). Since 2016, we have been awarded two European projects (the "ENABLE" H2020 ECSEL project 16 and the "CPS4EU" H2020 ECSEL project) involving major European automotive constructors and car suppliers. In these projects, Chroma is focusing on the embedded perception component (models and algorithms, including the certification issue). Chroma (A. Spalanzani) led also the ANR Hianic (2018-21) dealing with pedestrian-vehicle interaction for a safe navigation.
In this context, Chroma has two experimental vehicles equipped with various sensors (a Toyota Lexus and a Renault Zoe. , see. Fig. 2) , which are maintained by Inria-SED 17 and that allow the team to carry out experiments in realistic traffic conditions (Urban, road and highway environments). The Zoe car has been automated in December 2016, through our collaboration with the team of P. Martinet (IRCCyN Lab, Nantes), that allow new experiments in the team.
4.3 Service robotics with ground and aerial robots
Service robotics is an application domain quickly emerging, and more and more industrial companies (e.g., IS-Robotics, Samsung, LG) are now commercializing service and intervention robotics products such as vacuum cleaner robots, drones for civil applications, entertainment robots, etc. One of the main challenges is to propose robots which are sufficiently robust and autonomous, easily usable by non-specialists, and marked at a reasonable cost. We are involved in developing fleet of ground robots and aerial ones, see Fig. 2. Since 2016, we study solutions for 3D observation/exploration of complex scenes or environments with a fleet of UAVs (eg. BugWright2 H2020 project, Dynaflock Inria/DGA project) or ground robots (COMODYS FIL project 90).
A more recent challenge for the coming decade is to develop robotized systems for assisting elderly and/or disabled people. In the continuity of our work in the IPL PAL 18, we aim to propose smart technologies to assist electric wheelchair users in their displacements and also to control autonomous cars in human crowds (see Figure 6 for illustration). This concerns our recent "Hianic" ANR project. Another emerging application is humanoid robots helping humans at their home or work. In this context, we address the problem of NAMO (Navigation Among Movable Obstacles) in indoor environments (see PhD of B. Renault started on 2018). More generally we address navigation and object search with humanoids robots such as Pepper, in the context of the RoboCup-Social League competition.
5 Social and environmental responsibility
5.1 Footprint of research activities
- Due to the Covid, the vast majority of our trips for PhD defenses and for selection committees were replaced by videoconferences in 2021. While there is no question of systematizing the use of videoconferences, we changed our habits to offer a real alternative and seek a better compromise between environmental impact and user-friendliness.
- Some of our research topics involve high CPU usage. Some researchers in the team use the Grid5000 computing cluster, which guarantees efficient management of computing resources and facilitates the reproducibility of experiments. Some researchers in the team keep a log summarizing all the uses of computing servers in order to be able to make statistics on these uses and assess their environmental footprint more finely.
5.2 Impact of research results
- Romain Fontaine's thesis aims to develop algorithms for the efficient optimization of delivery rounds in the city. Our work is motivated by taking into account environmental constraints, set out in the report "Assurer le fret dans un monde fini" from The Shift Project (theshiftproject.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/Fret_rapport-final_ShiftProject_PTEF.pdf)
- Léon Fauste's thesis focuses on the design of a decision support tool to choose the scale when relocating production activities (work in collaboration with the Inria STEEP team). This resulted in a publication in collaboration with STEEP at ROADEF 32 and the joint organization of a workshop on the theme "Does techno-solutionism have a future?" during the Archipel conference which has been organized in June 2022 (archipel.inria.fr/).
- Christine Solnon has co-organized in Lyon (with Sylvain Bouveret, Nadia Brauner, Pierre Fouilhoux, Alexandre Marié, and Michael Poss), a one day workshop on environmental and societal challenges of decision making, on the 17th of November (sponsored by GDR RO and GDR IA).
- Chroma will organize in 2024 the national Archipel conference (archipel.inria.fr) on anthropocene challenges.
- Some of us are strongly involved in the development of INSA Lyon training courses to integrate DDRS issues (Christine Solnon is a member of the CoPil and the GTT on environmental and social digital issues). This participation feeds our reflections on the subject.
6 Highlights of the year
6.1 Awards
- Best Paper award IEEE ICARCV 2022 (17e Int. Conf. on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision) : Rabbia Asghar, Lukas Rummelhard, Anne Spalanzani and Christian Laugier, "Allo-Centric Occupancy Grid Prediction for Urban Traffic Scene Using Video Prediction Networks".
- Best Paper award IEEE IV 2022 (IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium) : Thomas Genevois, Jean-Baptiste Horel, Alessandro Renzaglia, and Christian Laugier, “Augmented Reality on LiDAR data: Going beyond Vehicle-in-the-Loop for Automotive Software Validation".
- Manon Predhumeau obtained the award of the Best PhD in computer science 2022 of Grenoble-Alpes-University.
6.2 New Projects
- ANR JCJC "AVENUE" coordinated by Alessandro Renzaglia (250 K€)
- ANR "MAMUT", Chroma is partner of the project, Christine Solnon coordinates our participation (128 K€ for Chroma partner, the total funding is 497 K€)
- ANR Annapolis, Chroma is partner of the project, Anne Spalanzani coordinates our participation (163 K€ for Chroma partner, the total funding is 831 K€)
- PEPR Agroécologie et numérique : Chroma is partner of the NINSAR project (New ItiNerarieS for Agroecology using cooperative Robots, 60 months). Olivier Simonin coordinates our participation (168 K€ for Chroma partner, the total funding is 2,16 M€)
6.3 Community activities
- Christian Laugier is appointed Editor-in-Chief of the IROS Conference Paper Review Board (CPRB) for the period 2023-25 (IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems).
- Christine Solnon has written the endorsement quote on the cover of the last Volume of the Art of Computer Programming (Volume 4B) written by Donald E. Knuth
- Olivier Simonin was a member of the international evaluation committee of 3IT Institute, University of Sherbrooke, Canada (incl. a one week visit in september).
6.4 Advancement in grade / career
- Anne Spalanzani is promoted to the grade of Professor (PR2)
- Olivier Simonin is promoted to the grade of Professor PREX1
7 New software and platforms
7.1 New software
7.1.1 CMCDOT
-
Keywords:
Robotics, Environment perception
-
Functional Description:
CMCDOT is a Bayesian filtering system for dynamic occupation grids, allowing parallel estimation of occupation probabilities for each cell of a grid, inference of velocities, prediction of the risk of collision and association of cells belonging to the same dynamic object. Last generation of a suite of Bayesian filtering methods developed in the Inria eMotion team, then in the Inria Chroma team (BOF, HSBOF, ...), it integrates the management of hybrid sampling methods (classical occupancy grids for static parts, particle sets for parts dynamics) into a Bayesian unified programming formalism , while incorporating elements resembling the Dempster-Shafer theory (state "unknown", allowing a focus of computing resources). It also offers a projection system of the estimated scene in the near future, to reference potential collisions with the ego-vehicle or any other element of the environment, as well as very low cost pre-segmentation of coherent dynamic spaces (taking into account speeds). It takes as input instantaneous occupation grids generated by sensor models for different sources, the system is composed of a ROS package, to manage the connectivity of I / O, which encapsulates the core of the embedded and optimized application on GPU Nvidia (Cuda), allowing real-time analysis of the direct environment on embedded boards (Tegra X1, X2). ROS (Robot Operating System) is a set of open source tools to develop software for robotics. Developed in an automotive setting, these techniques can be exploited in all areas of mobile robotics, and are particularly suited to highly dynamic and uncertain environment management (e.g. urban scenario, with pedestrians, cyclists, cars, buses, etc.).
-
Authors:
Amaury Nègre, Lukas Rummelhard, Jean-Alix David, Christian Laugier
-
Contact:
Christian Laugier
-
Partners:
CEA, CNRS
7.1.2 Ground Elevation and Occupancy Grid Estimator (GEOG - Estimator)
-
Keywords:
Robotics, Environment perception
-
Functional Description:
GEOG-Estimator is a system of joint estimation of the shape of the ground, in the form of a Bayesian network of constrained elevation nodes, and the ground-obstacle classification of a pointcloud. Starting from an unclassified 3D pointcloud, it consists of a set of expectation-maximization methods computed in parallel on the network of elevation nodes, integrating the constraints of spatial continuity as well as the influence of 3D points, classified as ground-based or obstacles. Once the ground model is generated, the system can then construct a occupation grid, taking into account the classification of 3D points, and the actual height of these impacts. Mainly used with lidars (Velodyne64, Quanergy M8, IBEO Lux), the approach can be generalized to any type of sensor providing 3D pointclouds. On the other hand, in the case of lidars, free space information between the source and the 3D point can be integrated into the construction of the grid, as well as the height at which the laser passes through the area (taking into account the height of the laser in the sensor model). The areas of application of the system spread across all areas of mobile robotics, it is particularly suitable for unknown environments. GEOG-Estimator was originally developed to allow optimal integration of 3D sensors in systems using 2D occupancy grids, taking into account the orientation of sensors, and indefinite forms of grounds. The ground model generated can be used directly, whether for mapping or as a pre-calculation step for methods of obstacle recognition or classification. Designed to be effective (real-time) in the context of embedded applications, the entire system is implemented on Nvidia graphics card (in Cuda), and optimized for Tegra X2 embedded boards. To ease interconnections with the sensor outputs and other perception modules, the system is implemented using ROS (Robot Operating System), a set of opensource tools for robotics.
-
Authors:
Amaury Nègre, Lukas Rummelhard, Lukas Rummelhard, Jean-Alix David, Christian Laugier
-
Contact:
Christian Laugier
7.1.3 Zoe Simulation
-
Name:
Simulation of INRIA's Renault Zoe in Gazebo environment
-
Keyword:
Simulation
-
Functional Description:
This simulation represents the Renault Zoe vehicle considering the realistic physical phenomena (friction, sliding, inertia, ...). The simulated vehicle embeds sensors similar to the ones of the actual vehicle. They provide measurement data under the same format. Moreover the software input/output are identical to the vehicle's. Therefore any program executed on the vehicle can be used with the simulation and reciprocally.
-
Authors:
Christian Laugier, Nicolas Turro, Thomas Genevois
-
Contact:
Christian Laugier
7.1.4 Hybrid-state E*
-
Name:
Path planning with Hybrid-state E*
-
Keywords:
Planning, Robotics
-
Functional Description:
Considering a vehicle with the kinematic constraints of a car and an environment which is represented by a probabilistic occupancy grid, this software produces a path from the initial position of the vehicle to its destination. The computed path may include, if necessary, complex maneuvers. However the suggested path is often the simpler and the shorter.
This software is designed to take benefit from bayesian occupancy grids such as the ones computed by the CMCDOT software.
- URL:
-
Authors:
Christian Laugier, Thomas Genevois
-
Contact:
Christian Laugier
-
Partner:
CEA
7.1.5 Pedsim_ros_AV
-
Name:
Pedsim_ros_AV
-
Keywords:
Simulator, Multi-agent, Crowd simulation, Autonomous Cars, Pedestrian
-
Scientific Description:
These ROS packages are useful to support robotic developments that require the simulation of pedestrians and an autonomous vehicle in various shared spaces scenarios. They allow: 1. in simulation, to pre-test autonomous vehicle navigation algorithms in various crowd scenarios, 2. in real crowds, to help online prediction of pedestrian trajectories around the autonomous vehicle.
Individual pedestrian model in shared space (perception, distraction, personal space, pedestrians standing, trip purpose). Model of pedestrians in social groups (couples, friends, colleagues, family). Autonomous car model. Pedestrian-autonomous car interaction model. Definition of shared space scenarios: 3 environments (business zone, campus, city centre) and 8 crowd configurations.
-
Functional Description:
Simulation of pedestrians and an autonomous vehicle in various shared space scenarios. Adaptation of the original Pedsim_ros model to simulate heterogeneous crowds in shared spaces (individuals, social groups, etc.). The car model is integrated into the simulator and the interactions between pedestrians and the autonomous vehicle are modeled. The autonomous vehicle can be controlled from inside the simulation or from outside the simulator by ROS commands.
- URL:
- Publications:
-
Contact:
Manon Predhumeau
-
Participants:
Manon Predhumeau, Anne Spalanzani, Julie Dugdale, Lyuba Mancheva
-
Partner:
LIG
7.1.6 S-NAMO-SIM
-
Name:
S-NAMO Simulator
-
Keywords:
Simulation, Navigation, Robotics, Planning
-
Functional Description:
2D Simulator of NAMO algorithms (Navigation Among Movable Obstacles) ROS compatible
-
Release Contributions:
Creation
-
Author:
Benoit Renault
-
Contact:
Benoit Renault
7.1.7 SimuDronesGR
-
Name:
Simultion of UAV fleets with Gazebo/ROS
-
Keywords:
Robotics, Simulation
-
Functional Description:
The simulator includes the following functionality : 1) Simulation of the mechanical behavior of an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle : * Modeling of the body's aerodynamics with lift, drag and moment * Modeling of rotors' aerodynamics using the forces and moments' expressions from Philppe Martin's and Erwan Salaün's 2010 IEEE Conference on Robotics and Automation paper "The True Role of Accelerometer Feedback in Quadrotor Control". 2) Gives groundtruth informations : * Positions in East-North-Up reference frame * Linear velocity in East-North-Up and Front-Left-Up reference frames * Linear acceleration in East-North-Up and Front-Left-Up reference frames * Orientation from East-North-Up reference frame to Front-Left-Up reference frame (Quaternions) * Angular velocity of Front-Left-Up reference frame expressed in Front-Left-Up reference frame. 3) Simulation of the following sensors : * Inertial Measurement Unit with 9DoF (Accelerometer + Gyroscope + Orientation) * Barometer using an ISA model for the troposphere (valid up to 11km above Mean Sea Level) * Magnetometer with the earth magnetic field declination * GPS Antenna with a geodesic map projection.
-
Release Contributions:
Initial version
-
Author:
Vincent Le Doze
-
Contact:
Vincent Le Doze
-
Partner:
Insa de Lyon
7.1.8 spank
-
Name:
Swarm Protocol And Navigation Kontrol
-
Keyword:
Protocoles
-
Functional Description:
Communication and distance measurement in an uav swarm
- URL:
-
Contact:
Stéphane d'Alu
-
Participant:
Stéphane d'Alu
7.2 New platforms
7.2.1 Chroma Aerial Robots platform
Participants: Olivier Simonin, Alessandro Renzaglia, Johan Faure.
This platform is composed of :
- Four quadrirotor PX4 Vision UAVs (Unmaned Aerial Vehicles), acquired 4 in 2021 and 2022. This platform is funded and used in the projects "Dynaflock" (Inria-DGA) and ANR "CONCERTO" (the team also owns 5 Parrot Bebop UAVs).
- Two outdoor inflatable aviaries of 6m(L) x 4m(l) x 5m(H) each.
- Two indoor inflatable aviaries of 5m(L) x 3m(l) x 2.5m(H) each.
8 New results
8.1 Bayesian Perception
Participants: Christian Laugier, Lukas Rummelhard, Andres Gonzalez Moreno, Jerome Lussereau, Thomas Genevois, Alessandro Renzaglia, Nicolas Turro, Amrita Suresh, Rabbia Asghar, Jean-Baptiste Horel.
Recognized as one of the core technologies developed within the team over the years (see related sections in previous activity report of Chroma, and previously e-Motion reports), the CMCDOT framework is a generic Bayesian Perception framework, designed to estimate a dense representation of dynamic environments and the associated risks of collision, by fusing and filtering multi-sensor data. This whole perception system has been developed, implemented and tested on embedded devices, incorporating over time new key modules. In 2022, this framework, and the corresponding software, has continued to be the core of many important industrial partnerships and academic contributions, and to be the subject of important developments, both in terms of research and engineering.
8.1.1 Extension of the CMCDOT framework to 3D Semantic Occupancy Grids
Participants: Andres Gonzalez Moreno, Lukas Rummelhard, Christian Laugier.
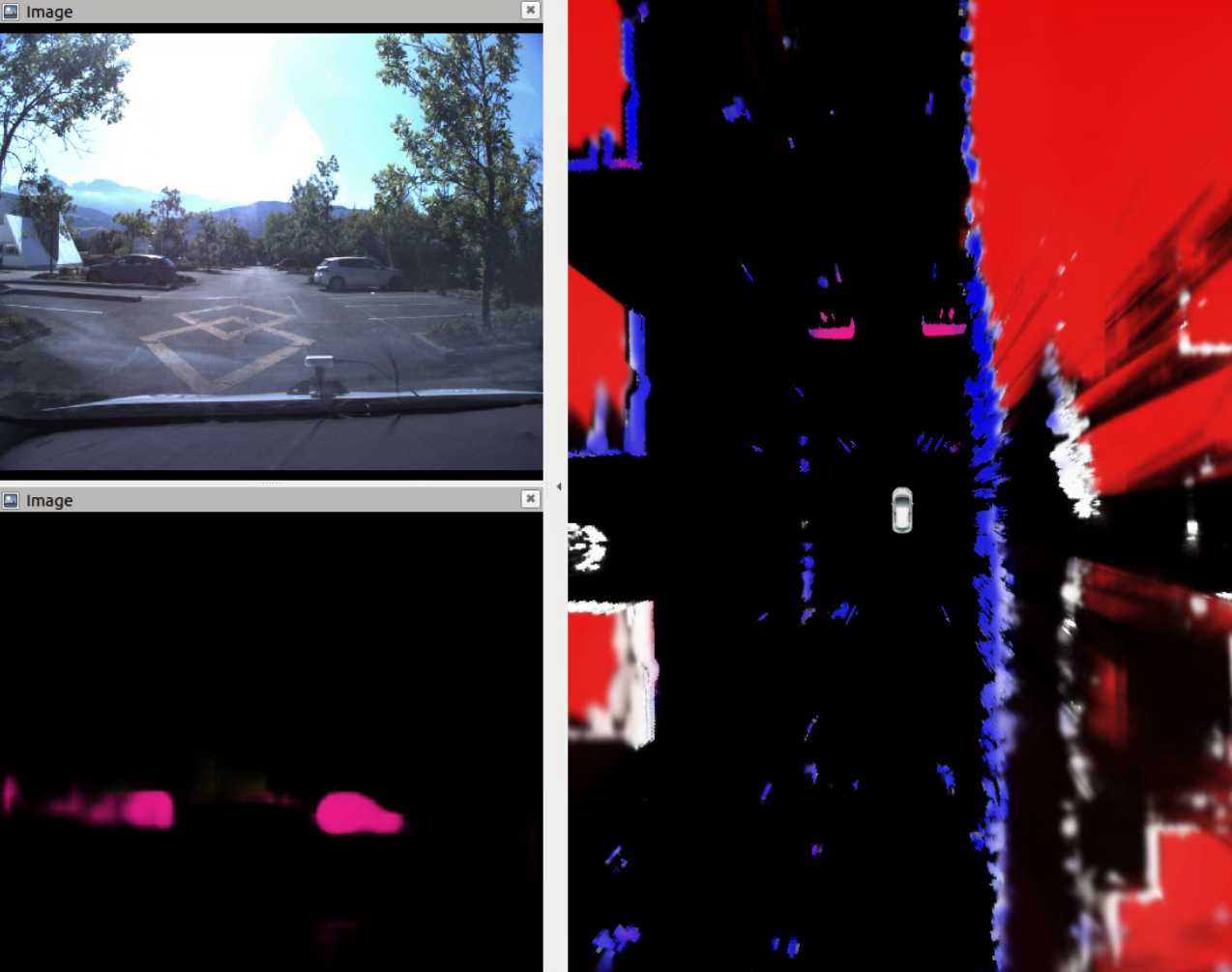
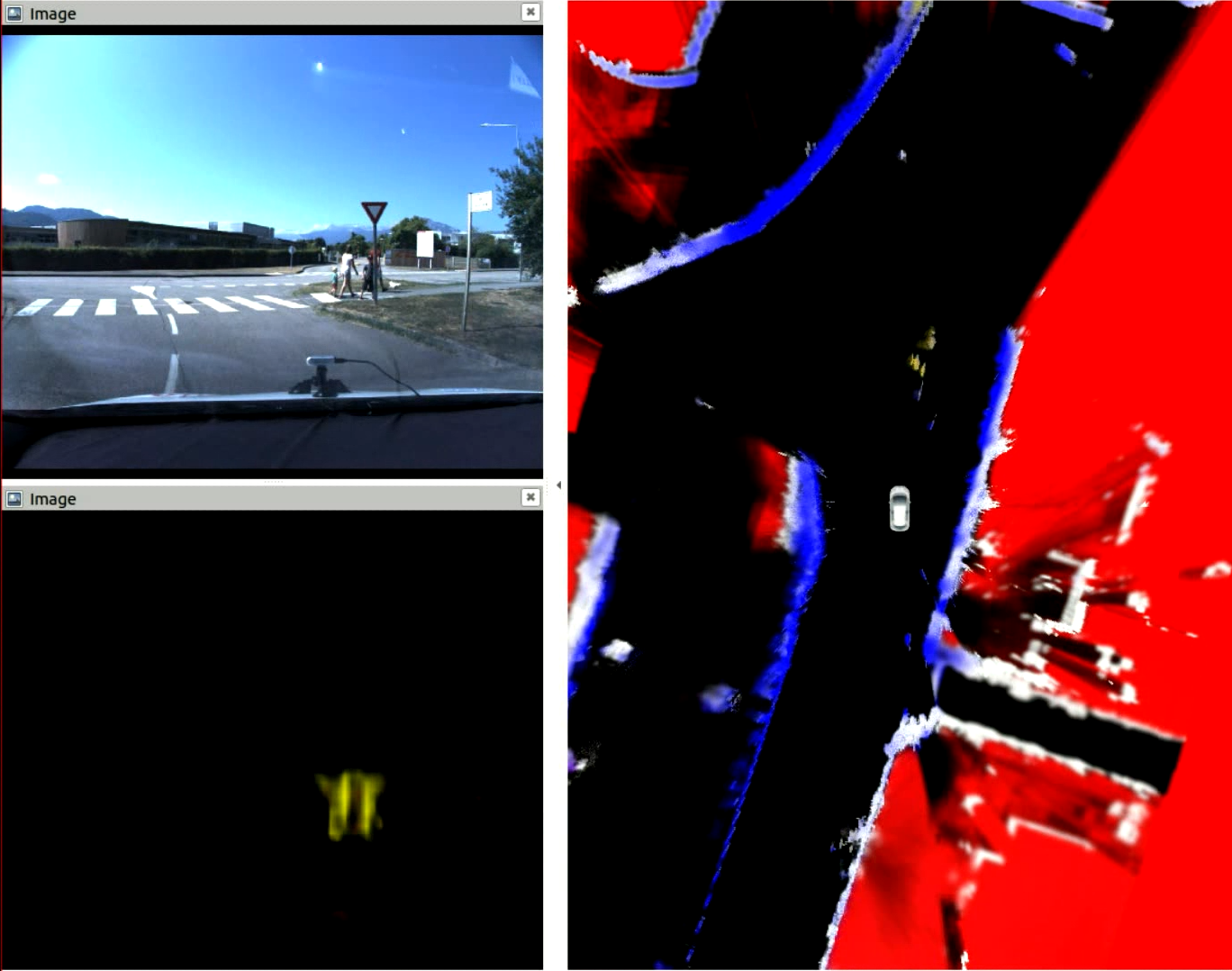
Following 2021 work, the CMCDOT-framework expansion to 3D semantic states, instead of 2D occupancy-only grids, has continued. Such an evolution includes the reorganization and software adaptation of the architecture and the various component parts, the introduction of modules for generating semantic occupation grids based on artificial intelligence, the extension of grid fusion functions to 3D and semantics, as well as software and algorithmic developments in grid filtering 27. Now integrated up to the filtering of estimated states, the system is able to perceive semantic states (pedestrian, car, etc.) using cameras, project them onto occupation grids, merge them with information from 'other sensors (lidar, ultrasound, etc.), and filter them over time, opening up many possibilities for future developments to improve the perception, dynamic estimations and predictions, or the quality, safety and acceptability of the navigation of autonomous systems (see illustrations fig. 3).
8.1.2 Cooperative Perception with Dynamic Occupancy Grids
Participants: Andres Gonzalez Moreno, Rabbia Asghar, Jerome Lussereau, Nicolas Turro, Lukas Rummelhard, Christian Laugier.
In order to expand coverage and overall perception capabilities of an embedded perception system, data exchange between sensing agents is a valuable solution. If occupancy grids are a well-suited tool to fuse data from heterogeneous sources with different viewpoints, the mere size of these structures makes their efficient communication a real challenge. On an experimental plateform consisting of a infrastructure unit equipped with 2 lidars, a Nvidia TX2 card executing the CMCDOT framework and VTX capabilities, and a connected autonomous Zoe plateform (with its own sensors and CMCDOT framework running), two main methods of grid transmission from the infrastructure to the autonomous vehicle have been developed and tested. Following 2021 work, a new communication framework has been developped, which extracts objects from the occupancy grid of the infrastructure, sends object information to the vehicle using VTX communication, then reconstructs the corresponding occupancy grid based on these (taking into account added uncertainties) and fuses it with local perception. The communication software has been implemented based on the ETSI TR 103 562 protocol from the European Telecomunications Standards Institute, Intelligent Transport Systems.
8.1.3 Augmented Reality and realistic pedestrian simulation tools for advanced automotive software testing
Participants: Thomas Genevois, Andres Gonzalez Moreno, Nicolas Turro, Lukas Rummelhard, Christian Laugier.
In 2021, CHROMA developed an augmented reality system on sensor data from the experimental Zoe. This system makes it possible during tests of the vehicle perception and navigation software to realistically introduce virtual elements in the real environment of the vehicle, and in its perception. It allows to validate the simulation tools associated with the vehicle by integrating them into an augmented reality scene and comparing them to their real equivalents, and also, it makes it possible to envisage much richer test scenes, with many pedestrians and vehicles, without any risk of collision, while guaranteeing the repeatability of the tests. In 2022, this method and the results on the experimental vehicle were published 19 at the "IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV22)" and were rewarded with the event "best paper award". Several works were also carried out to make the best use of this augmented reality technology.
In order to simulate realistic pedestrians, the pedestrian crowd simulator SPACiSS, developed by the team, was interfaced with the augmented reality tool on the experimental vehicle (see Fig. 4). SPACiSS is a state-of-the-art simulator, dedicated to the simulation of pedestrians and an autonomous vehicle in a shared space, based on agent-based modeling for pedestrian trajectories around an autonomous vehicle14. This simulator is particularly distinguished by its ability to generate realistic pedestrian behavior in social interactions between pedestrians and interactions with a vehicle.

A clear visualization of the augmented reality scenes was needed, to interpret and present the experimental results generated with this tool. Indeed, the augmented reality tool intervenes in real time on the data from the vehicle sensors (LiDAR and camera) but does not generate a clear visualization of the experiment from a point of view external to the car, making it difficult to understand the performance of the navigation software during collision avoidance tests with multiple targets. In order to generate an external view of the augmented scene, infrastructure cameras have been connected, calibrated, and can now be used to display real-time views of the augmented reality scene from outside the vehicle.
Thanks to this developments, the experimental vehicle and environment now constitute a state-of-the-art experimental platform for augmented reality testing, allowing for realistic autonomous vehicle navigation tests in densely-populated urban areas (see Fig. 5).
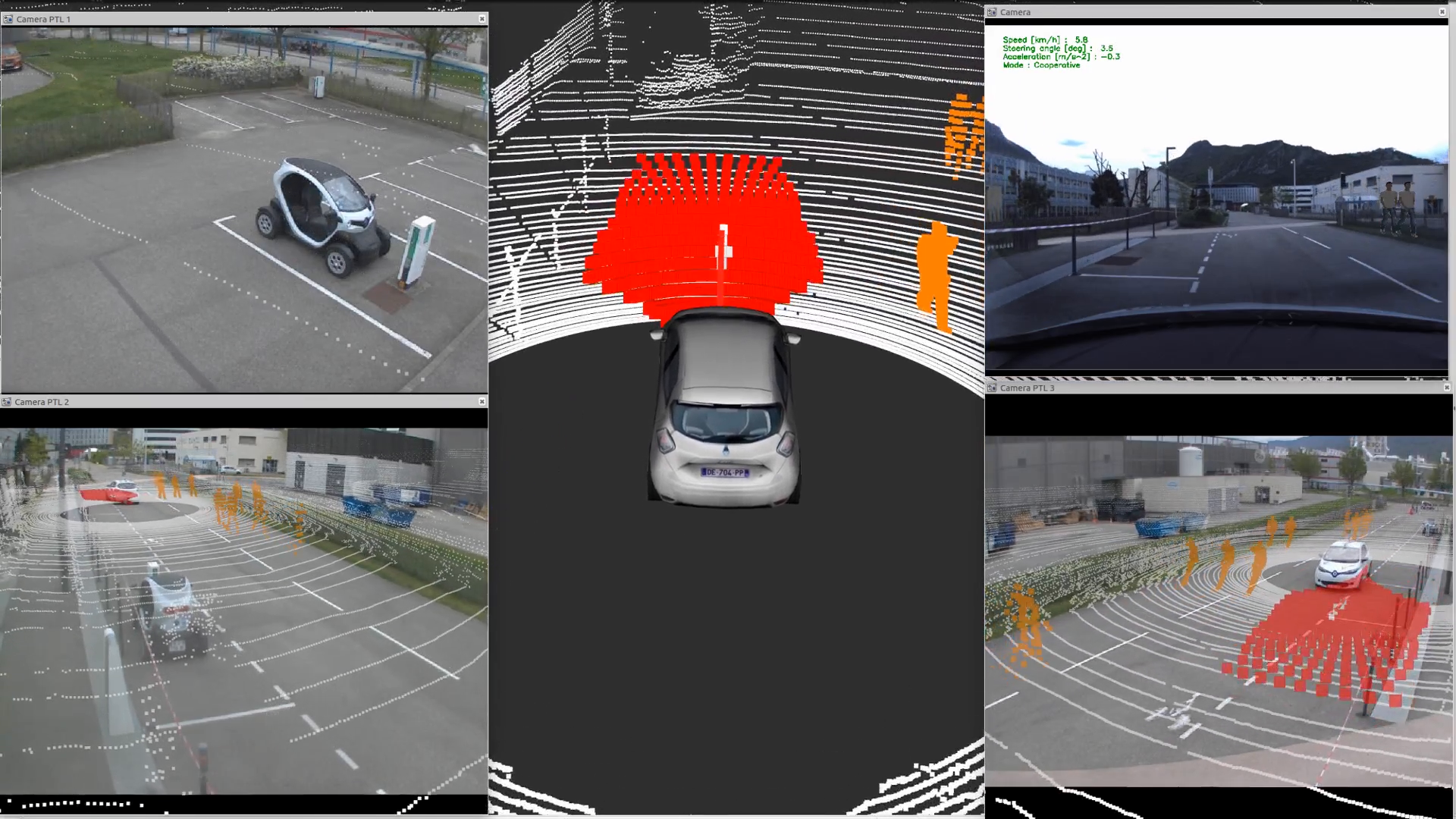
Presentation of the tools used to analyze the behavior of the experimental vehicle during an augmented reality test.
8.1.4 Development of an industrial AIV, light perception and navigation systems
Participants: Thomas Genevois, Amrita Suresh, Lukas Rummelhard, Christian Laugier.
CHROMA has been working with the company AKEOPLUS, in a new use case, in the scope of the regional R&D project Booster MoovIT, to continue the development of the embedded version of perception and navigation software. This project involves developing a versatile AIV (Autonomous Intelligent Vehicle) dedicated to the logistics of warehouses and industrial workshops. While AKEOPLUS develops the mechanics, the electronics, the basic automatisms of the robot as well as the supervision system and the user interface, CHROMA develops the functions of perception, path planning and local navigation. The jointly developed AIV should be tested in the workshop of a third-party company, Spanninga. If this specific use case implies new developments, these will also benefit the other applications of the software suite built around the CMCDOT. Such developments included in 2022 an evolution of the ground estimation software, allowing for a refined estimation of the ground slope, and the generation of an accessibility map according to this slope for a robot, then integrated in the perception and navigation framework. This evolution has been experimentally validated with the project sensors.
8.1.5 Validation of AI-based algorithms in autonomous vehicles
Participants: Jean-Baptiste Horel, Alessandro Renzaglia, Pierrick Koch, Anshul Paigwar, Radu Mateescu [Convecs], Wendelin Serwe [Convecs], Christian Laugier.
In the last years, there has been an increasing demand for regulating and validating intelligent vehicle systems to ensure their correct functioning and build public trust in their use. Yet, the analysis of safety and reliability poses a significant challenge. More and more solutions for autonomous driving are based on complex AI-based algorithms whose validation is particularly challenging to achieve. An important part of our work has been recently devoted to tackle this problem, finding new suitable approaches to validate probabilistic algorithms for perception and decision making in autonomous driving, and investigating how simulations and experiments in controlled environment can help to solve this challenge. This activity, started with our participation in the European project Enable-S3 (2016-2019), is now continuing with the PRISSMA project, started in April 2021, where we participate in collaboration the the Inria Convecs team. This project, funded by the French government in the framework of the “Grand Défi: Sécuriser, certifier et fiabiliser les systèmes fondés sur l’intelligence artificielle”, regroups several companies and public institutes in France and tackles the challenge of the validation and certification of artificial intelligence based solutions for autonomous mobility.
Within this context, our main work in 2022 has been focused on the automatic generation of large numbers of relevant critical scenarios for autonomous driving simulators 21. This approach is based on the generation of behavioral conformance tests from a formal model (specifying the ground truth configuration with the range of vehicle behaviors) and a test purpose (specifying the critical feature to focus on). The obtained abstract test cases cover, by construction, all possible executions exercising a given feature, and can be automatically translated into the inputs of autonomous driving simulators. We illustrate our approach by generating thousands of behavior trees for the CARLA simulator for several realistic configurations. An extension of this work, where we model check the traces of the simulation runs, combining the advantages of temporal logic verification and quantitative analyses to validate a probabilistic collision risk estimation, has been recently accepted for pubblication in the Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems 72.
8.2 Situation Awareness & Decision-making for Autonomous Vehicles
Participants: Ozgur Erkent, David Sierra-González, Anshul Paigwar, Christian Laugier, Manuel Alejandro Diaz-Zapata, Alessandro Renzaglia, Jilles Dibangoye, Luiz Serafim-Guardini, Anne Spalanzani, Wenqian Liu, Abhishek Tomy, Khushdeep Singh Mann, Rabbia Asghar, Lukas Rummelhard, Gustavo Salazar-Gomez, Olivier Simonin.
In this section, we present all the novel results in the domains of perception, motion prediction and decision-making for autonomous vehicles.
8.2.1 Situation Understanding and Motion Forecasting
Participants: David Sierra-González, Anshul Paigwar, Ozgur Erkent, Christian Laugier.
Forecasting the motion of surrounding traffic is one of the key challenges in the quest to achieve safe autonomous driving technology. Current state-of-the-art deep forecasting architectures are capable of producing impressive results. However, in many cases, they also output completely unreasonable trajectories, making them unsuitable for deployment. In 2022, we have developed a deep forecasting architecture that leverages the map lane centerlines available in recent datasets to predict sensible trajectories; that is, trajectories that conform to the road layout, agree with the observed dynamics of the target, and react to the presence of surrounding agents. To model such sensible behavior, the proposed architecture first predicts the lane or lanes that the target agent is likely to follow. Then, a navigational goal along each candidate lane is predicted, allowing the regression of the final trajectory in a lane- and goal-oriented manner. Our experiments in the Argoverse dataset show that our architecture achieves performance on-par with lane-oriented state-of-the-art forecasting approaches and not far behind goal-oriented approaches, while consistently producing sensible trajectories. This work was published at IEEE ITSC 2022 30.
Current work is focused on bridging the gap between semantic grid prediction approaches and motion forecasting. The goal is to leverage the semantic information of the environment that can be extracted from the cameras to improve the performance of the proposed centerline-based motion forecasting methods.
8.2.2 Semantic Grid Generation from Camera and LiDAR Sensor Fusion
Participants: Manuel Alejandro Diaz-Zapata, David Sierra-González, Ozgur Erkent, Christian Laugier, Jilles Dibangoye, Olivier Simonin.
Continuing the work towards semantic grid generation, during 2022 a novel method was created called LiDAR-Aided Projective Transform Network (LAPTNet) 18. By using depth information taken from a LiDAR sensor, this approach is able to project image features to a bird's-eye-view which are then used to estimate semantic grids that can describe the layout of the scene around a car.
This method was later extended to work with multiple image scales taken from the image encoder (LAPT-FPN), as well as the addition of a LiDAR-dependent branch (LAPT-PP) to further process the point clouds incoming from the LiDAR. The final proposed method uses these two extensions (LAPT-FPN-PP) to predict semantic grids in real time (25 FPS), and is able to outperform other competing approaches that use only camera or LiDAR information, or a fusion of both. LAPT-FPN-PP achieves a result close to the state-of-the-art for vehicle semantic grid segmentation while being 3.7x faster. This work has been accepted for publication at ICRA 2023.
8.2.3 Lidar-RGB Sensor Fusion with Transformers for Semantic Grid Prediction
Participants: Gustavo Salazar-Gomez, David Sierra-González, Manuel Alejandro Diaz-Zapata, Anshul Paigwar, Wenqian Liu, Ozgur Erkent, Christian Laugier.
Semantic grids are a succinct and convenient approach to represent the environment for mobile robotics and autonomous driving applications. While the use of Lidar sensors is now generalized in robotics, most semantic grid prediction approaches in the literature focus only on RGB data. In the work performed we explore different fusion algorithms and methods, and we propose an approach for semantic grid prediction that uses a transformer architecture to fuse Lidar sensor data with RGB images from multiple cameras. Our proposed method, TransFuseGrid, first transforms both input streams into topview embeddings, and then fuses these embeddings at multiple scales with Transformers. We evaluate the performance of our approach on the nuScenes dataset.
The results of this work are presented in the Master thesis “Transformer-based Lidar-RGB Fusion for Semantic Grid Prediction in Autonomous Vehicles” 44, and as a paper at the 17th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision (ICARCV), Dec 2022, Singapore 28.
In the next steps, we explore algorithms for semantic grid prediction, relying only on camera data and transformers, understanding the role of different positional encoding approaches.
8.2.4 Allo-centric Occupancy Grid Prediction for Urban Traffic Scene Using Video Prediction Networks
Participants: Rabbia Asghar, Lukas Rummelhard, Anne Spalanzani, Christian Laugier.
Prediction of dynamic environment is crucial to safe navigation for an autonomous vehicle. Urban traffic scenes are particularly challenging to forecast due to complex interactions between various dynamic agents, such as vehicles and vulnerable road users. Previous approaches have used ego-centric occupancy grid maps to represent and predict dynamic environments. However, these predictions suffer from blurriness, loss of scene structure at turns, and vanishing of agents over longer prediction horizon. In this work, we propose a novel framework to make long-term predictions by representing the traffic scene in a fixed frame, referred as allo-centric occupancy grid. This allows for the static scene to remain fixed and to represent motion of the ego-vehicle on the grid like other agents'. We study the allo-centric grid prediction with different video prediction networks and validate the approach on the real-world Nuscenes dataset. The results demonstrate that the allo-centric grid representation significantly improves scene prediction, in comparison to the conventional ego-centric grid approach.
This work has been published and presented at the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision (ICARCV) 16.
8.2.5 Lidar-Camera Sensor Fusion for Object Detection and Tracking
Participants: Wenqian Liu, Ozgur Erkent, David Sierra-González, Christian Laugier.
Modern tracking by detection algorithms heavily rely on accurate detections. Yet to precisely localize the objects in the three-dimensional space is still very challenging for 3D detectors. One of the key reasons is the inherent sparsity and noise present in point clouds when using LiDAR as the sole input sensor. However, RGB camera images, as a natural complementary modality for point clouds, possess higher resolution and richer color and texture cues. Conversely, 3D structural information obtained from point clouds can compensate the lack of depth information from RGB images. As a result, we propose to adopt Transformers models to generate comprehensive and contextual fused features from both modalities and develop our Lidar-Camera fusion techniques to improve the performance of the existing 3D object detectors and trackers. The proposed models are trained and evaluated on NuScenes dataset. Our approach outperforms the baseline Lidar-only object detection models under the same experimental setups.
8.2.6 End-to-End Driving using Attention based Reinforcement Learning
Participants: Khushdeep Singh Mann, Abhishek Tomy, Anshul Paigwar, Alessandro Renzaglia, Christian Laugier.
One important area of research in autonomous driving is the extraction of semantic representations through the fusion of many sensor modalities. The semantic representations can now be utilized to drive policies for executing end-to-end decision making thanks to previous research from the team, such as "LAPTNet: LiDAR-Aided Perspective Transform Network" 18. Under no traffic and busy traffic scenarios, we retrieved semantic representation for training attention-based deep reinforcement learning (RL) policies. The ego-vehicle picks up driving habits and methods for interacting with other agents. In comparison to vanilla RL policies, we show that self-attention and cross-attention systems provide superior performance. We intend to conduct further experiments in future work and release the results as a conference paper.
8.2.7 Transformer-based Event Camera Disparity Estimation
Participants: Abhishek Tomy, Khushdeep Singh Mann, Anshul Paigwar, Alessandro Renzaglia, Christian Laugier.
We continue our work from 2021 on disparity estimation from stereo event-based cameras. Within this project's scope, fundamental design choices that would lead to improved performance in the case of depth estimation using an event camera are explored. To achieve state-of-art results in the event-based depth estimation task, the type of event representation and transformer based network architecture were experimented on. In the case of an input representation, event voxels (stacking based on time) and stacking based on the number of events (SBN) are explored to determine if these representations can lead to improved generalization to various conditions. Both these representations for depth estimations are compared with concentrating the events to a single channel by the state-of-the-art "concentration network" model. For model architecture, a transformer-based network that can handle the temporal information in events is being designed to handle sparse events from the camera.
8.2.8 Detection and Tracking Model Deployment on Chroma's Experimental Driving Platform
Participants: Khushdeep Singh Mann, Abhishek Tomy, David Sierra-Gonzalez, Christian Laugier.
Detection and tracking of the surrounding agents is a crucial activity for an autonomous vehicle. Currently, the software packages deployed on the Zoe experimental platform lack 3D object detection. In this project, a 3D object detection and tracking pipeline is being deployed. For 3D object detection, a PointPillars model trained on the nuScenes dataset is used for detection. For object tracking, a constant acceleration based Kalman filter methodology with greedy matching is used to track and associate detected objects. For deployment, the deep-learning models are optimized using TensorRT for faster inference on real-time applications.
In future work, the detection and tracking packages will be combined with prediction and planning modules for safe autonomous navigation. Recent research work from the team on semantic grid prediction will be translated to a deployable solution for generating semantic grids and will be one of the building blocks for the planning module. All these packages would complete the autonomous driving stack and enable real-world experiments on the Zoe experimental platform.
8.3 Robust state estimation (Sensor fusion)
Participants: Agostino Martinelli.
This research is the follow up of Agostino Martinelli's investigations carried out during the last seven years, which mainly consisted in the derivation of the analytical solution of the unknown input observability problem. This is the problem of obtaining a simple analytical criterion to check the observability of the state that characterizes a nonlinear system when its dynamics are driven by inputs which are unknown and act as disturbances. This was an open problem, formulated during the 1960's by the automatic control community and that remained unsolved for half century.
In December 2018, Martinelli was invited by the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM) to write a book with the solution of this problem. This was the main work during 2019 89. The book contains a general analytical solution of this open problem. The solution is an algorithm that automatically provides the observability of a given system (technically speaking it provides the observability codistribution), independently of its complexity and nonlinearity, and in the presence of unknown inputs. On the other hand, this solution is based on an important assumption that, in the book, was called canonicity with respect to the unknown inputs. In addition, even in the case of systems that satisfy this assumption, the convergence criterion of the algorithm provided in 89 can fail in some special cases.
The research carried out during 2021-2022 has been focused on the following three main topics:
- Obtaining a general convergence criterion of the algorithm in the canonical case.
- Dealing with systems that do not satisfy the canonicity assumption.
- Investigating the problem of unknown input reconstruction, which is strongly related to the problem of state observability in the presence of unknown inputs.
All these objectives have been successfully accomplished and, at the moment, published on arXiv 88. The same results have been accepted for publication, in the format of a very long paper, by the Journal of Information Fusion and, part of these results, are also conditionally accepted for publication on the Transaction on Automatic Control.
We exhaustively dealt with the systems that do not belong to the category of the systems that are canonical with respect to their unknown inputs. We provided new definitions of this concept and we obtained a more general solution that can also be applied to systems that are not canonical with respect to their unknown inputs. In addition, we showed that, in some cases, we can transform a non canonical system into a canonical system. We called these systems canonizable. The new proposed solution can deal with the case where the system is not canonical and not even canonizable. This new solution is also provided in the form of a new algorithm. Finally, as a simple consequence of these results, we also provided the answer to the problem of unknown input reconstruction which is intimately related to the problem of state observability.
8.4 Motion-planning in dense pedestrian environments
Under the coordination of Anne Spalanzani, we study new motion planning algorithms to allow robots/ vehicles to navigate in human populated environment while predicting pedestrians' motions. We model pedestrians and crowd behaviors using notions of social forces and cooperative behavior estimations. We investigate new methods to build safe and socially compliant trajectories using theses models of behaviors. We propose proactive navigation solutions as well as deep learning ones. The works of year 2021 are presented below.

A scene of an Autonomous Vehicle with pedestrians
8.4.1 Modelling crowds and autonomous vehicles using Extended Social Force Models
Participants: Manon Predhumeau (LIG Grenoble & Chroma), Anne Spalanzani, Julie Dugdale (LIG Grenoble).
The focus of this work has been on the realistic simulation of crowds in shared spaces with an autonomous vehicle (AV), see Fig. 6. We proposed an agent-based model for pedestrian reactions to an AV in a shared space, based on empirical studies and the state of the art. The model includes an AV with Renault Zoé car’s characteristics, and pedestrians’ reactions to the vehicle. The model extends the Social Force Model with a new decision model, which integrates various observed reactions of pedestrians and pedestrians groups. We performed a qualitative and quantitative evaluation of the proposed model, through comparisons of the simulated trajectories with ground truth trajectories. The proposed model reproduces well the various pedestrians behaviors: running to cross, stopping to wait without deviating, staying in social group to avoid the AV. The model can be used for predicting pedestrians’ displacement, linear velocity, orientation, and approach distance around the AV in fundamental interactions (AAMAS'21 100).
We implemented this model using Pedsim_ros and proposed an open source simulation tool to help the robotic community with AV developments. The simulator integrates various observed pedestrians behaviours, with individual pedestrians as well as pedestrian groups with four different types of relationships (SCS'20 99). Complex shared spaces situations have been modeled, which require the interaction of a large number of pedestrians responding to the AV movement. The simulated AV can be controlled by an external ROS module, so that AV navigation algorithms can be tested in various realistic, crowded shared space environments, before real-world experiments. Moreover, simulations can reproduce real world scenes and can run faster than real-time to help live prediction of pedestrian trajectories around the AV.
8.4.2 Proactive Navigation for navigating dense human populated environments
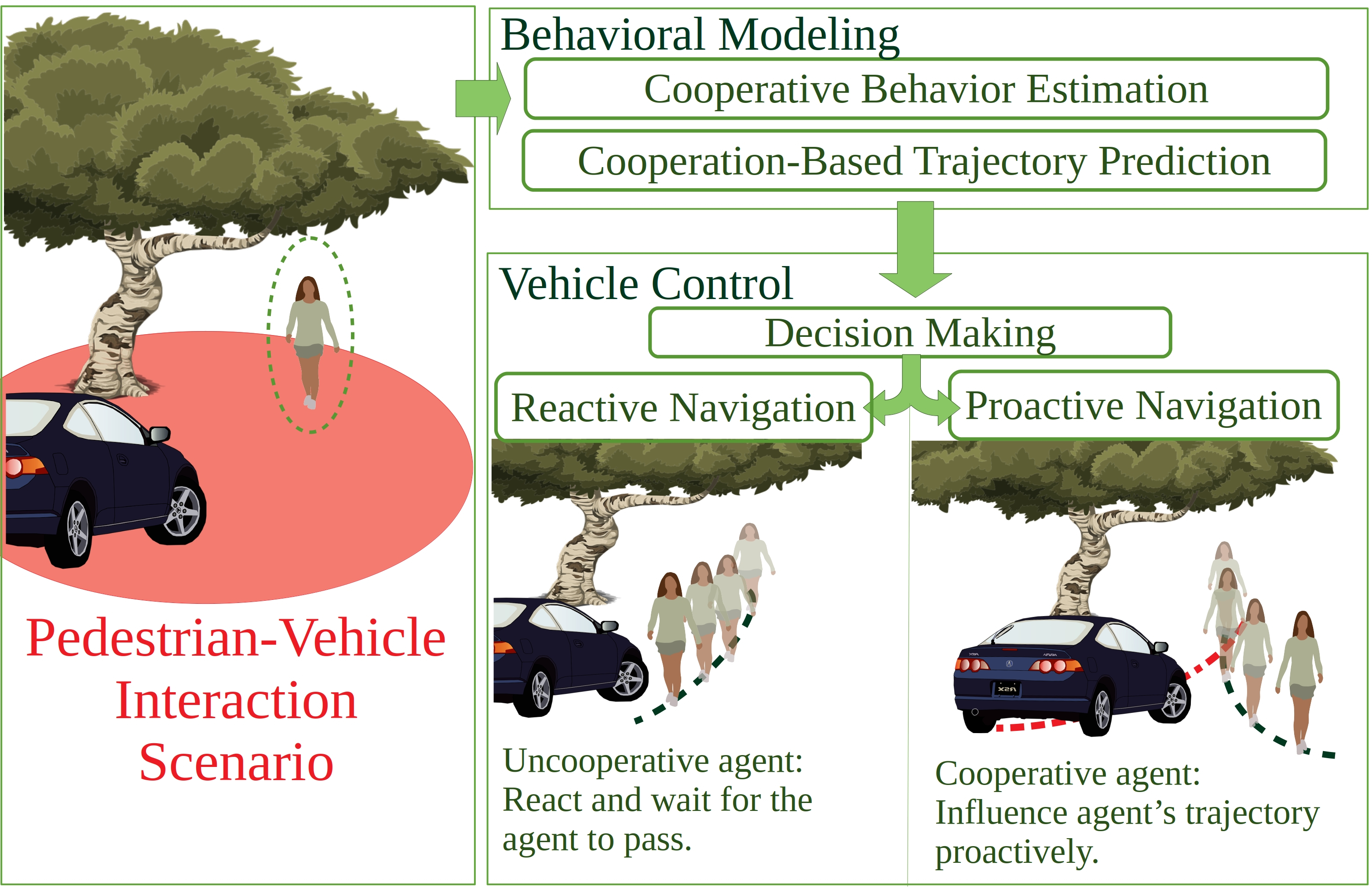
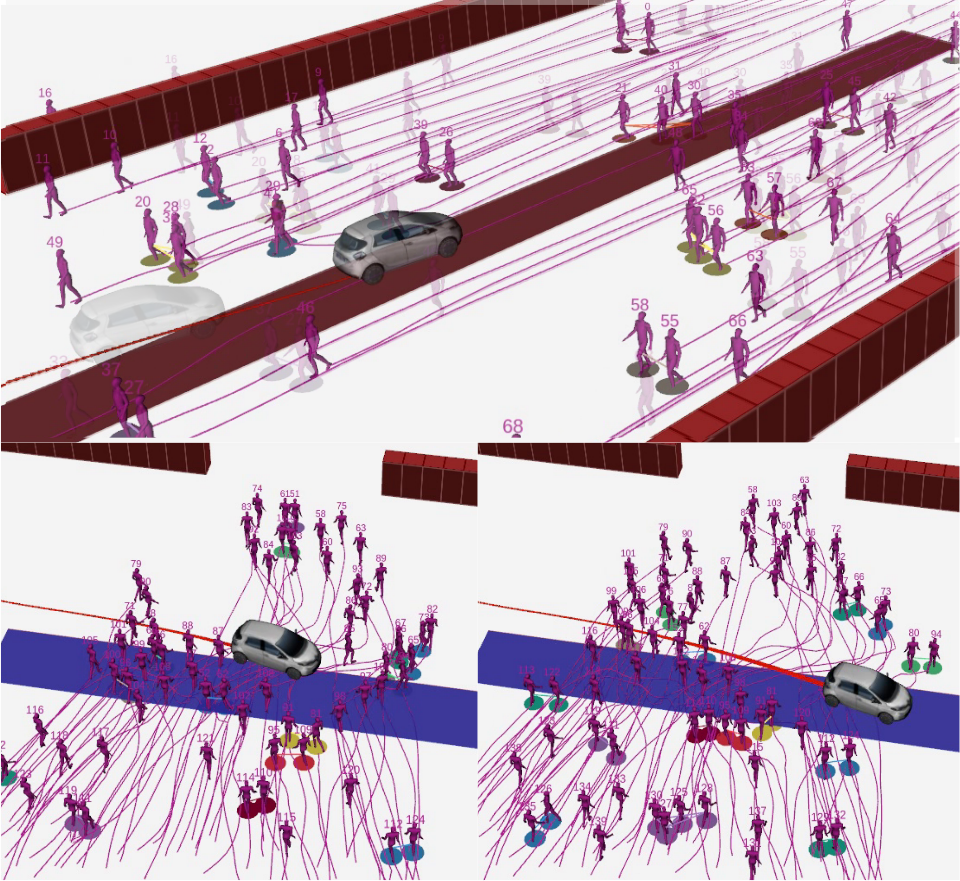
Participants: Maria Kabtoul, Anne Spalanzani, Philippe Martinet [Chorale, Inria Sophia Antipolis].
Developing autonomous vehicles capable of navigating safely and socially around pedestrians is a major challenge in intelligent transportation. This challenge cannot be met without understanding pedestrians’ behavioral response to an autonomous vehicle, and the task of building a clear and quantitative description of the pedestrian to vehicle interaction remains a key milestone in autonomous navigation research. As a step towards safe proactive navigation in a space shared with pedestrians, we started to introduce in 2018 a pedestrian-vehicle interaction behavioral model. The model estimates the pedestrian’s cooperation with the vehicle in an interaction scenario by a quantitative time-varying function. Using this cooperation estimation the pedestrian’s trajectory is predicted by a cooperation-based trajectory planning model (see Fig. 7.a). Both parts of the model are tested and validated using real-life recorded scenarios of pedestrian-vehicle interaction. The model is capable of describing and predicting agents’ behaviors when interacting with a vehicle in both lateral and frontal crossing scenarios. In early 2019, we used this cooperation based behavioral model to design a proactive longitudinal velocity controller. The suggested velocity control strategy enabled the vehicle to cooperate and proactively interact with its surrounding rather than merely reacting to the behavior of the pedestrians. This resulted in more natural driving patterns, avoiding the sub-optimal navigation solutions which result in over-reactive methods. The method is tested and validated in lateral interactions with a flow of pedestrians. The method showed a high gain in the time to reach the goal in comparison with reactive navigation, while ensuring the pedestrians safety. In 2020, we integrated the previous navigation system with the PedSim simulator under ROS. Next, we worked on a proactive and human-like maneuvering system to deploy the steering control part of the navigation system. We adopted a two-step approach. In the first step, the navigation space is explored proactively and an optimal navigation channel is found using a fuzzy logic model. This proactive dynamic channel is guaranteed to exist even in dense scenarios where obstacle free paths do not exist. In the second step, a human-like steering is adapted using a Quintic transition path and a sliding mode control approach. The resulting system is tested under ROS in combination with the longitudinal velocity controller and the cooperation-based behavioral model. The resulting system is validated in both frontal and lateral interactions with dense crowds (see Fig. 7.b). The system results in major advantage in the travel time avoiding the freezing of the vehicle, while ensuring the pedestrian’s safety. This work has been published in ITSC'20 75, ICRA'20 76 and ICRA'22 23
8.5 Online planning and learning for robot navigation
8.5.1 Deep-Learning for vision-based navigation
Participants: Pierre Marza (PhD. student CITI & LIRIS), Edward Beeching, Christian Wolf (NaverLabs europe), Olivier Simonin, Laetitia Matignon (LIRIS/Lyon 1), Jilles Dibangoye.
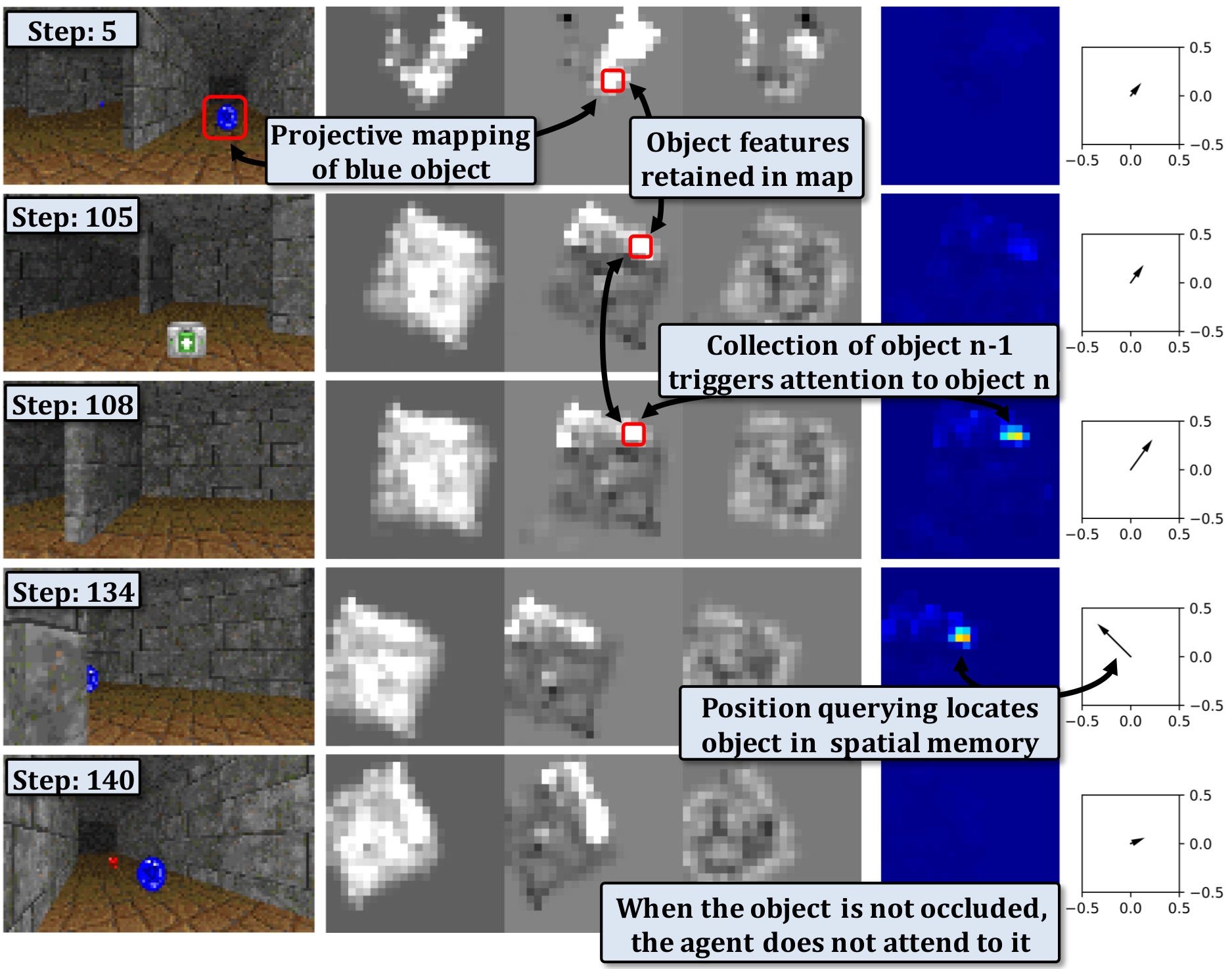


Our goal is the automatic learning of robot navigation in complex environments based on specific tasks and from visual input. The robot automatically navigates in the environment in order to solve a specific problem, which can be posed explicitly and be encoded in the algorithm (e.g. find all occurences of a given object in the environment, or recognize the current activities of all the actors in this environment) or which can be given in an encoded form as additional input, like text. Addressing these problems requires competences in computer vision, machine learning/AI, and robotics (navigation and paths planning).
A critical part for solving these kind of problems involving autonomous agents is handling memory and planning. Many control problems in partially observed 3D environments involve long term dependencies and planning. Solving these problems requires agents to learn several key capacities: spatial reasoning (exploring the environment and learning spatio-temporal regularities) and semantic mapping (discovering semantics from interactions). While solutions exist for semantic mapping and semantic SLAM 60, 116, a more interesting problem arises when the semantics of objects and their affordances are not supervised, but defined through the task and thus learned from reward.
PhD thesis of Edward Beeching (2018 - May 2022, Inria grant): After showing that through visualizations an agent can learn to map relevant objects in its spatial memory without any supervision purely from reward (see Fig. 8.a and 52, 51, 50) we proposed a 3D training framework. E. Beeching developed the Godot RL Agents, which is an interface between DeepRL algorithms and the Godot Game Engine (Linietsky 2014). This new framework allows to create 2D & 3D games to learn behaviors with automated testing and multi-process parallel training. E. Beeching defended his doctoral thesis on May 3, 2022 38.
PhD thesis of Pierre Marza (since 2021). In the context of the REMEMBER AI Chair, Pierre Marza started a PhD on the subject "Large-scale learning of high-level navigation skills for autonomous agents in 3D environments" (supervised by C. Wolf, L. Matignon and O. Simonin). A key question is the ability to learn representations with minimal human intervention and annotation. From the Egocentric Map approach, we introduced supplementary supervision in the form of auxiliary tasks (see Fig. 8.b) designed to favor the emergence of spatial perception capabilities in agents trained for a goal-reaching downstream objective. This allowed us to win the MultiON Challenge at CVPR2021 Embodied AI Workshop. And in 2022, we published the results in 25 (presenting our architecture with the auxiliary tasks).
8.5.2 Navigation Among Movable Obstacles: extension of NAMO to multi-robot and social constraints
Participants: Benoit Renault, Jacques Saraydaryan, Olivier Simonin.
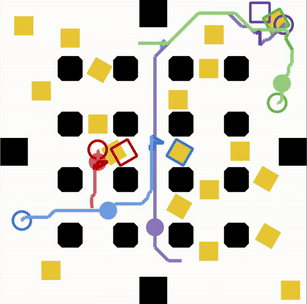
In 2018 we started to study the NAMO planning problem (Navigation Among Movable Obstacles). Since 2019, the PhD thesis of Benoit Renault aims to extend NAMO in two directions:
- Defining Social-NAMO, by considering where obstacles should be optimally moved with regards to space access. We have defined new spatial cost functions and extended existing NAMO algorithms with the ability to maintain area accesses (connectivity) for humans and robots, see IROS publication 102. We also developed a simulator for NAMO, and its extensions, called S-NAMO-SIM (see Fig. 9.a), now used by the community.
- Defining Multi-robot NAMO (MR-NAMO). It consists in generalizing the problem to robots that can move the objects of the environment in order to reach their individual goal positions. We have proposed a first coordination strategy based on local rules. We have shown that considering the social cost we introduced with S-NAMO offers a significant gain for solving MR-NAMO because of the rearranging it provides (see Fig. 9.b).
In 2022, a particular effort has been made to explore the limits of our S-NAMO based multi-robot deadlock solving approach. More complex situations/environments have been analyzed and a global conflict/deadlock decision-architecture has been established. This is part of the thesis writing conduced by B. Renault in 2022. He will defend his doctoral thesis about May 2023.
8.6 Swarm of UAVs: decentralized control, path-planning and communication
8.6.1 Multi-UAV Exploration and Visual Coverage of 3D Environments
Participants: Alessandro Renzaglia, Olivier Simonin.
Multi-robot teams, especially when involving aerial vehicles (UAVs 19), are extremely efficient systems to help humans in collecting information on large and complex environments. In these scenarios, cooperative coverage and exploration are two fundamental problems with numerous important applications, such as mapping, inspection of complex structures, and search and rescue missions. In both cases, the robots' goal is to navigate through the environment and cooperate to acquire new information to carry out the mission as fast as possible.
Following our recent results on these problems 105, 104, in the last year we focused on a strictly related path planning problem where a fleet of UAVs must use both prior information and online gathered data to efficiently inspect large surfaces such as ship hulls and water tanks 20. This work is conducted in the framework of the H2020 European project BugWright2, where one central use-case is focused on corrosion detection and inspection on cargo ships. In our case, UAVs can detect corrosion patches and other defects on the surface from low-resolution images. If defects are detected, they get closer to the surface for a high-resolution inspection. The prior information provides expected defects locations and is affected by both false positives and false negatives. The mission objective is to prioritize the close-up inspection of defected areas while keeping a reasonable time for the coverage of the entire surface. In this work, we propose two solutions to this problem: a coverage algorithm that divides the problem into a set of Traveling Salesman Problems and a cooperative frontier approach that introduces frontier utilities to incorporate the prior information. In an additional work on this subject 22, which involved a Master internship, we tackled a variation of the classic mCPP (multi-robot coverage path planning) where weights are introduced to represent different coverage times for each cell in the environment. To solve this problem, we presented a solution based on a modified version of the DARP algorithm 77. The proposed approach cannot only solve the weighted version of the mCPP, but it also obtains an increased convergence rate and a decreased convergence time with respect to the original version of the DARP algorithm.
Starting from January 2023, the cooperative exploration and 3D reconstruction of complex unknown environment with a fleet of aerial vehicles is also the main subject of the new AVENUE project (ANR JCJC) and will thus continue to be an important line of research in the team.
8.6.2 Decentralized control of swarm of UAVs: Flocking models
Participants: Alexandre Bonnefond [Phd. Inria/CITI],, Isabelle Guerrin-Lassous [LIP/Inria/Dante Lyon 1],, Olivier Simonin, Johan Faure.
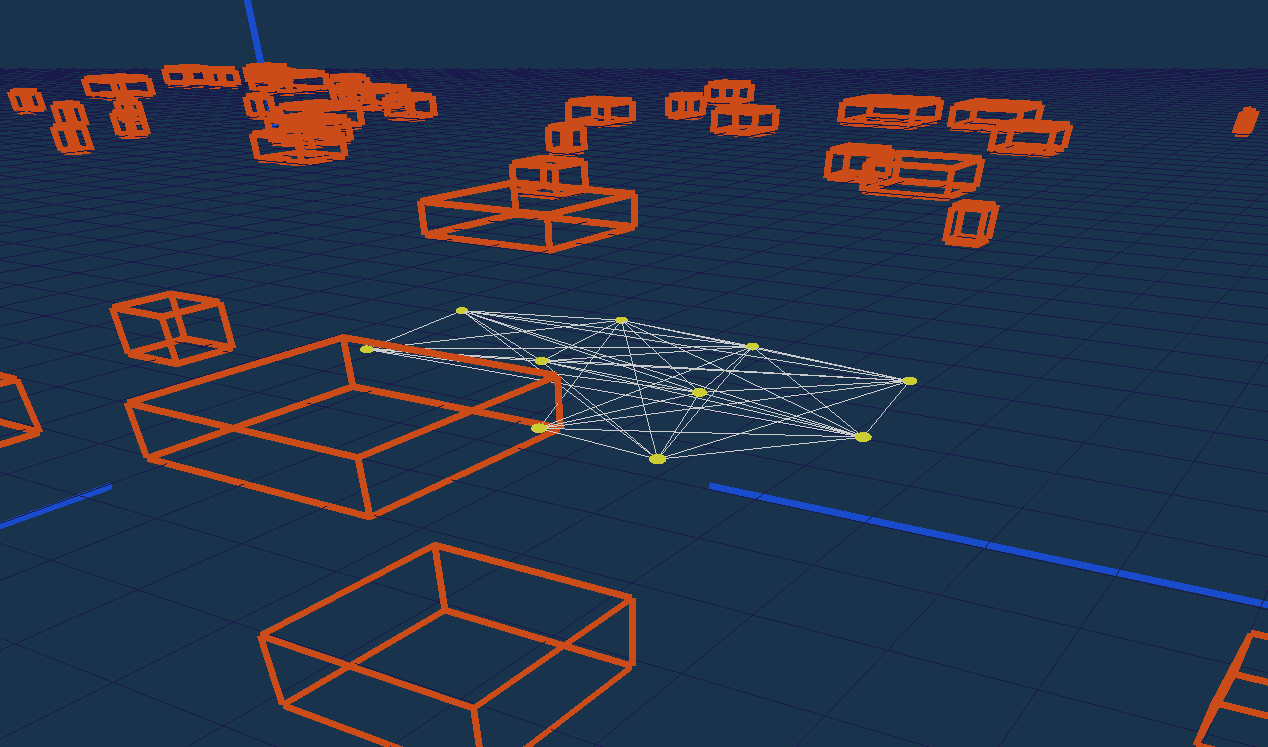

This work is conduced through the Inria/DGA "AI" project "DYNAFLOCK" (2019-23). It funds the PhD thesis of Alexandre Bonnefond.
We study communication-based flocking models (decentralized swarm navigation) and propose extensions to improve their abilities to deal with environments having obstacles. Often depicted as robust systems, there is yet a lack of understanding how flocking models compare and how they are impacted by the communication quality when they exchange control data. After extending and combining two standard models, Olfati-Saber 91 and Vásárhelyi et al. 117, we showed their limits (see IROS 2021 54 and Fig. 10.a). In 2022, we proposed a new model, called APR (Asymetric Pressure Regulation). This model introduces an individual measure of pressure allowing to define a new flocking control able to anticipate dangerous/close agents interactions (this work has been submited to the JINT journal).
In 2022, we also continued on developing flocking simulations with the Gazebo 3D simulator (involving mainly Johan Faure). We also prepared real experiments with PX4 Vision UAVs embedding UWB-based distance measurement.
8.6.3 Communication and localization in swarm of UAVs
Participants: Olivier Simonin, Isabelle Guerin-Lassous [Inria/Lyon 1 Dante team], Stephane d'Alu, Johan Faure, Hervé Rivano.
We continued to work within the CONCERTO ANR project ("mobilité Contrôlée et cOmmunicatioNs effiCaces dans une flottE de dRones auTo-Organisée"). In 2022, our work focused on designing a UAVs platform designed for outdoor experiments. After acquiring PX4 Vision UAVs we proposed to design outdoor inflatable aviaries. The design was entrusted to AirCaptif (Michelin) compagny. Fig. 10.b shows one of our two aviaries. Each offers a 6m x 4m x 5m volume, they can be attached to double the volume.
In the same time, we continued to work on the Ultra-Wide Band (UWB) technology, which allows to measure distance between robots and to estimate their localisation to UWB beacons. In the following of our early work 124, we designed supports allowing now to exploit UWB-measures on PX4 Vision UAVs. This work is mainly conduced by Stephane d'Alu and Johan Faure. In the end of 2022, we started to experiment with UAVs and to prepare a first autonomous flocking with 3 PX4 Vision, exploiting only relative distance measures (a publication is in preparaion).
8.7 Multi-Agent Sequential Decision-Making under Uncertainty
This research is the follow up of a group led by Jilles S. Dibangoye carried out during the last five years, which include foundations of sequential decision making by a group of cooperative or competitive robots or more generally artificial agents. To this end, we explore combinatorial, convex optimization and reinforcement learning methods.
8.7.1 Optimally solving zero-sum games using centralized planning for decentralized control theory
Participants: Aurelien Delage [PhD Student], Jilles S. Dibangoye, Olivier Buffet [Inria Nancy, Larsen], Vincent Thomas [Inria Nancy, Larsen], Abdallah Saffidine [Univ. New South Whales], Christopher Amato [Univ. New Hampshire], François Charpillet [Inria Nancy, Larsen].
During the last three years, we investigated deep and standard reinforcement learning for solving systems with multiple agents and different information structures. Our preliminary results include:
- (Theoretical) – As an extension of 63 in the competitive cases, we characterize the optimal solution of two-player fully and partially observable stochastic games.
- (Theoretical) – We further exhibit new underlying structures of the optimal solution for both non-cooperative two-player settings with information asymmetry, one agent sees what the other does and sees.
- (Algorithmic) – We extend a non-trivial procedure for computing such optimal solutions.
This work aims at reinforcing a recent theory and algorithms to optimally solving a two-person zero-sum POSGs (zs-POSGs). That is, a general framework for modeling and solving two-person zero-sum games (zs-Games) with imperfect information. Our theory builds upon a proof that the original problem is reducible to a zs-Game—but now with perfect information. In this form, we show that the dynamic programming theory applies. In particular, we extended Bellman equations 53 for zs-POSGs, and coined them maximin (resp. minimax) equations. Even more importantly, we demonstrated Von Neumann & Morgenstern’s minimax theorem 120119 holds in zs-POSGs. We further proved that value functions—solutions of maximin (resp. minimax) equations—yield special structures. More specifically, the optimal value functions are Lipchitz-continuous. Together these findings allow us to extend planning techniques from simpler settings to zs-POSGs. To cope with high-dimensional settings, we also investigated low-dimensional (possibly non-convex) representations of the approximations of the optimal value function. In that direction, we extended algorithms that apply for convex value functions to lipschitz value functions. This research direction lead to many publications in different avenues 58 along with technical reports 59.
PhD thesis of Aurelien Delage (since Sept. 2020, ANR JCJC PLASMA). This thesis aims at extending ideas conducted on cooperative multi-agent partially observable systems to pure competitive ones.
8.7.2 HSVI fo zs-POSGs using Concavity, Convexity and Lipschitz Properties
Participants: Delage Aurelien [PhD Student], Jilles S. Dibangoye, Olivier Buffet [Inria Nancy, Larsen].
Dynamic programming and heuristic search are at the core of state-of-the-art solvers for sequential decision-making problems. In partially observable or collaborative settings (e.g., POMDPs and Dec-POMDPs), this requires introducing an appropriate statistic that induces a fully observable problem as well as bounding (convex) approximators of the optimal value function. This approach has succeeded in some subclasses of 2-player zero-sum partially observable stochastic games (zs-POSGs) as well, but failed in the general case despite known concavity and convexity properties, which only led to heuristic algorithms with poor convergence guarantees. We overcome this issue, leveraging on these properties to derive bounding approximators and efficient update and selection operators, before deriving a prototypical solver inspired by HSVI that provably converges to an -optimal solution in finite time, and which we empirically evaluate. This opens the door to a novel family of promising approaches complementing those relying on linear programming or iterative methods 61.
8.7.3 Global Min-Max Computation for alpha-Hölder Zero-Sum Games
Participants: Delage Aurelien [PhD Student], Jilles S. Dibangoye, Olivier Buffet [Inria Nancy, Larsen].
Min-max optimization problems recently arose in various settings. From Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to aerodynamic optimization through Game Theory, the assumptions on the objective function vary. Motivated by the applications to deep learning and especially GANs, most recent works assume differentiability to design local search algorithms such as Gradient Descend Ascent (GDA). In contrast, this work will only require -Hölder properties to tackle general game-theoretic problems with poor continuity as- sumptions. Focusing on the example of problems in which max and min optimization variables live in simplices, we provide a simple algorithm, based on Deterministic Optimistic Optimization (DOO), relying on an outer min-optimization using the solutions of an inner max-optimization. The algorithm is shown to converge in finite time to an -global optimum. Experimental validations are given and the time complexity of our algorithm is studied.
8.7.4 Optimally Solving Decentralized POMDPs Under Hierarchical Information Sharing
Participants: Sayil Barish [MS Intern], Albert David, Xie Yuxuan [BS Intern], Olivier Buffet [Inria Nancy, Larsen], Jilles S. Dibangoye.
This work is the result of an effort to provide a strong theory for optimally solving decentralized decision-making problems, represented as decentralized partially observable Markov decision processes (Dec-POMDPs), with tractable structures 121. This work describes core ideas of multi-agent reinforcement learning algorithms for decentralized partially observable Markov decision processes (Dec-POMDPs) under hierarchical information sharing. That is the dominant management style in our society—each agent knows what her immediate subordinate knows. In this case, we prove backups to be linear due to (normal-form) Bellman optimality equations being for the first time specified in extensive form. Doing so, one can sequence agent decisions at every point in time while still preserving optimality; hence paving the way for the first optimal -learning algorithm with linear-time updates for an important subclass of Dec-POMDPs. That is a significant improvement over the double-exponential time required for normal-form Bellman optimality equations, in which updates of agent decisions are performed in sync every point in time. Experiments show algorithms utilizing extensive instead of normal-form Bellman optimality equations can be applied effectively to much larger problems.
8.7.5 Optimally Solving Decentralized POMDPs: The Sequential Central Learning Approach
Participants: Johan Peralez [Post-doc], Albert David, Olivier Buffet [Inria Nancy, Larsen], Jilles S. Dibangoye.
The centralized learning for simultaneous decentralized execution paradigm emerged as the state-of-the-art approach to -optimally solving a simultaneous- move decentralized partially observable Markov decision process, but the scalability remains a significant issue. This paper presents a novel—yet more scalable—alternative, namely sequential central learning for simultaneous decentralized execution. This methodology pushes the applicability of Bellman’s principle of optimality further, raising three new properties. First, it allows a central learner to reason upon sufficient sequential statistics instead of prior simultaneous ones. Next, it proves that -optimal value functions are piecewise linear and convex in sufficient sequential statistics. Finally, it drops the time complexity of the backup operators from double exponential to linear at the expense of longer planning horizons. Besides, it makes it easy to use single-agent methods—e.g., a reinforcement learning algorithm enhanced with these findings applies while still preserving its asymptotic convergence guarantees. Experiments on standard 2- as well as -agent benchmarks from the literature against state-of-the-art -optimal solvers confirm the superiority of the novel paradigm.
8.7.6 Stable Reinforcement Learning Methods
Participants: Jilles S. Dibangoye, Nicolas Marchand [GIPSA lab, Grenoble], Ahmad Hably [GIPSA lab, Grenoble], Estéban Carvalho [PhD Student, GIPSA lab, Citi lab], Vincent Andrieu [LAGEPP, Lyon], Daniele Astolfi [LAGEPP, Lyon], Giacomo Casadei [LAGEPP, Lyon], Madiha Nadri [LAGEPP, Lyon], Samuele Zoboli [PhD Student, LAGEPP, Citi lab].
This recent research project is at the intersection of three closely related research fields: optimal control, machine learning, and mobile robotics. In this project, we try to find the best compromise between control methodologies to provide stability guarantees and machine learning methodologies that can scale up and converge towards a locally optimal solution. Applications of this hybrid methodology concern mobile robotics, including the driving of drones at very high speed. Two PhD. theses have been started on this problem the last year.
PhD thesis of Estéban Carvalho (since Oct. 2019). The first thesis focuses on high-speed navigation for UAVs in collaboration with the laboratory GIPSA. The goal of this PhD is to develop safe and aggressive piloting algorithms for UAVs. Piloting algorithms will be designed on event-switched control coupled with AI routines to cope with unmodeled and uncertain part of the system to reach as much as possible the limits of aggressive flight.
PhD thesis of Samuele Zoboli (since Jul. 2020, ANR DELICIO). In control theory, a natural approach for the design of stabilizing control is to consider a linear approximation around the operating point of the dynamic system. In this way, it is possible to design control laws that are optimal and which guaranteed stability for the linearized system. However, this behavior is only guaranteed for the original system around this operating point (local approach). The aim of this PhD thesis is to develop new real time algorithms (contol law and estimation algorithms for dynamical systems) that combines tools coming from control theory and reinforcement learning.
8.7.7 Neural Enhanced Control for Quadrotor Linear Behavior Fitting
Participants: Estéban Carvalho [PhD Student, GIPSA lab, Citi lab], Pierre Susbielle [GIPSA lab, Grenoble], Ahmad Hably [GIPSA lab, Grenoble], Jilles S. Dibangoye, Nicolas Marchand [GIPSA lab, Grenoble].
Designing an efficient autopilot for a quadrotor can be a very long and tedious process. This comes from the complex nonlinear dynamics that rule the flying robot behavior as battery discharge, blade flapping, gyroscopic effect, frictions, etc. In this paper we proposed to use a traditional cascaded control architecture enhanced with Deep Neural Network (DNN). The idea is to easily setup a control algorithm using linear cascaded laws and then correct unmodelled dynamics and approximations made during the linear control design with the DNN. The tuning process is reduced to choice of proportional and derivative gains of each control loop. The approach is tested in the ROS/Gazebo simulation environment and experimentally in a motion capture room. Results confirm that the methodology significantly improves the performance of linear approaches on nonlinear quadrotor system. This work was published at the IEEE International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems 17.
8.7.8 Event-based Neural Learning for Quadrotor Control
Participants: Estéban Carvalho [PhD Student, GIPSA lab, Citi lab], Pierre Susbielle [GIPSA lab, Grenoble], Ahmad Hably [GIPSA lab, Grenoble], Nicolas Marchand [GIPSA lab, Grenoble], Jilles S. Dibangoye.
The design of a simple and adaptive flight controller is a real challenge in aerial robotics. A simple flight controller often generates a poor flight tracking performance. Furthermore, adaptive or learning algorithms are costly in time and resources, and may cause instability problems, for instance in the presence of disturbances. In this paper, we propose an event-based neural learning strategy that combines the use of a standard cascaded flight controller enhanced using a deep neural network that learns the disturbances to improve the tracking performance. The strategy relies on two events: one allowing the improvement of tracking errors and a second to ensure the stability of the closed-loop system. After a validation of the proposed strategy in a ROS/Gazebo simulation environment, its effectiveness is confirmed on real experiments, in the presence of wind disturbance. This work is under review at Autonomous Robots.
8.7.9 Locally Asymptotically Stable Deep Actor-Critic Algorithms For Quadratic Cost Setpoint Optimal Control Problems
Participants: Samuele Zoboli [PhD Student, LAGEPP, Citi lab], Vincent Andrieu [LAGEPP, Lyon], Daniele Astolfi [LAGEPP, Lyon], Giacomo Casadeic [LAGEPP, Lyon], Madiha Nadri [LAGEPP, Lyon], Jilles S. Dibangoye.
Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) algorithms showed surprising capabilities in solving complex nonlinear control problems. However, these capabilities come at a price. For instance, they construct controllers with only practical stability properties. On the contrary, Lyapunov-based controllers provide strong stability guarantees by exploiting the knowledge about the dynamic model. A recent work proved DRL algorithms, enhanced with such dynamic model information, locally guarantee desirable properties. The present work circumvents the requirement of local dynamic model's knowledge by learning it from data. The resulting DRL algorithms achieve the best of both worlds: local strong stability properties and improved domain of attraction compared to classical Lyapunov-based methods. Experiments over three benchmarks support our claims.
8.8 Constraint Optimisation problem
8.8.1 Constraint Programming
Participants: Jean-Yves Courtonne [Inria STEEP], François Delobel [LIMOS], Léon Fauste, Pascal Lafourcade [LIMOS], Luc Libralesso, Mathieu Mangeot [Inria STEEP], Loïc Rouquette, Christine Solnon.
In many of our applications, we have to solve constrained optimization problems (COPs) such as vehicle routing problems, or multi-agent path finding problems, for example. These COPs are usually NP-hard, and we study and design algorithms for solving these problems. We more particularly study approaches based on Constraint Programming (CP), that provides declarative languages for describing these problems by means of constraints, and generic algorithms for solving them by means of constraint propagation. In 87, we show how to automatically generate efficient CP models for solving differential cryptanalysis problems given the description of a symmetric block cipher.
PhD thesis of Loïc Rouquette (Oct. 2019 - Nov. 2022). This thesis was funded by the ANR project DeCrypt, that aims at designing declarative languages (based on CP) for solving cryptanalysis problems. Loïc has designed new propagation algorithms that are integrated in the Choco CP library 107, new CP models for mounting related-key differential attacks of Rijndael 26 and Boomerang attacks on Feistel ciphers 79.
PhD thesis of Léon Fauste (since Sept. 2021). This thesis is funded by Ecole Normale Supérieure Paris Saclay and it is co-supervised by Mathieu Mangeot, Jean-Yves Courtonne (from Inria STEEP team) and Christine Solnon. The goal of the thesis is to design new tools for choosing the best geographical scale when relocating productive activities, and the context of this work is described in 32. During the first months of his thesis, Léon has designed a first Integer Linear Programming (ILP) model described in 34.
8.8.2 Multi-Robot Path Planning with cable constraints
Participants: Xiao Peng [PhD. student CITI], Christine Solnon, Olivier Simonin.
The research is done within the context of the european project BugWright2 that aims at designing an adaptable autonomous multi-robot solution for servicing ship outer hulls.
PhD thesis of Xiao Peng (since Nov. 2020). The goal of this PhD thesis is to design algorithms for planning a set of mobile robots, each attached to a flexible cable, to cover an area with obstacles. In 97, we formally define the Non-Crossing MAPF (NC-MAPF) problem and show how to compute lower and upper bounds for this problem by solving well known assignment problems, we introduce a Variable Neighbourhood Search approach for improving the upper bound, and we introduce a CP model for solving the problem to optimality. In 92, we extend this approach to the case of non point-sized robots.
8.8.3 Vehicle routing problems
Participants: Romain Fontaine [PhD Student CITI], Thierry Garaix [LIMOS, Saint Etienne], Omar Rifki [LIMOS, Saint Etienne], Jilles S. Dibangoye, Christine Solnon.
The research is done within the context of the transportation challenge and funded by INSA Lyon.
Integration of traffic conditions:
In classical vehicle routing problems, travel times between locations to visit are assumed to be constant. This is not realistic because traffic conditions are not constant throughout the day, especially in an urban context. As a consequence, quickest paths (i.e., successions of road links), and travel times between locations may change along the day. To fill this lack of realism, cost functions that define travel times must become time-dependent. These time-dependent cost functions are defined by exploiting data coming from sensors, and the frequency of the measures as well as the number and the position of the sensors may have an impact on tour quality.
PhD thesis of Romain Fontaine (since Oct. 2020). State-of-the-art approaches for solving vehicle routing problems hardly scale when considering time-dependent cost functions. The goal of the PhD thesis of Romain is to design new algorithms based on dynamic programming. Constraints (such as, for example, time-windows or pickup-and-delivery constraints) are exploited to prune states, and new bounds and heuristics are designed to guide the search. The approach is described in 71.
Theoretical and empirical study of routing problems.
We study the impact of time-window constraints on the satisfiability and the difficulty of routing problems in 106.
9 Bilateral contracts and grants with industry
9.1 Bilateral contracts with industry
9.1.1 Toyota Motor Europe (2006 - 2023)
Participants: Christian Laugier, David Sierra González, Özgür Erkent, Jilles Dibangoye, Christian Wolf.
The contract with Toyota Motors Europe is a joint collaboration involving Toyota Motors Europe, Inria and ProbaYes. It follows a first successful short term collaboration with Toyota in 2005. This contract aims at developing innovative technologies in the context of automotive safety. The idea is to improve road safety in driving situations by equipping vehicles with the technology to model on the fly the dynamic environment, to sense and identify potentially dangerous traffic participants or road obstacles, and to evaluate the collision risk. The sensing is performed using sensors commonly used in automotive applications such as cameras and lidar.
This collaboration has been extended in 2018 for 4 years (period 2018-2021) and Toyota provides us with an experimental vehicle Lexus equipped with various sensing and control capabilities. Several additional connected technical contracts have also been signed, and an exploitation license for the CMCDOT software has been bought by Toyota in 2018.
9.1.2 Sumitomo Electric Industries (2020-23)
Participants: Christian Laugier, Lukas Rummelhard (SED), Andres Gonzalez Moreno, Rabbia Asghar, Jerome Lussereau, Nicolas Turro (SED).
R&D project to develop and demonstrate multi-modal perception using communicating infrastructures, data exchange and fusion between such infrastructure and mobile autonomous vehicles, and the added value of such architecture. Based on embedded Bayesian perception systems (CMCDOT framework), the project aims to develop long-term prediction and risk assessment.9.2 Bilateral grants with industry
9.2.1 Renault (2019 - 2022)
Participants: Luiz Alberto Guardini Serafim, Christian Laugier, Anne Spalanzani, Philippe Martinet.
This contract was linked to the PhD Thesis of Luiz Alberto Guardini Serafim (Cifre Thesis). The objective is to address the open problem of emergency obstacle avoidance in complex traffic situations (for ADAS or AD applications) using planning in grid occupancy.9.2.2 IRT Nanoelec – Security of Autonomous Vehicles project (2018 - 2020), Security of Industrial Robotics (2021-2023)
Participants: Christian Laugier, Lukas Rummelhard (SED), Jerome Lussereau, Andres Gonzalez Moreno, Thomas Genevois, Nicolas Turro (SED).
Security of Autonomous Vehicles, then Security of Industrial Robotics, is a project supported by PIA in the scope of the program PULSE of IRT Nanoelec. The objective of this project is to integrate, develop and promote technological bricks of context capture, for the safety of the autonomous vehicle. Building on Embedded Bayesian Perception for Dynamic Environment, Bayesian data fusion and filtering technologies from sets of heterogeneous sensors, these bricks make it possible to secure the movements of vehicles, but also provide them with an enriched and useful representation for autonomy functions themselves. In this context, various demonstrators embedding those technology bricks are developed in cooperation with industrial partners.
9.2.3 MeanWhile (2021 - 2023)
Participants: Fabrice Jumel, Jacques Saraydaryan.
This contract is a BPI France funding between MeanWhile compagny and CPE Lyon. The project concerns the development of an indoor geolocation device for third-party equipment for a fleet of autonomous mobile robots. It funds an engineer position (18 months CPE/Meanwhile).10 Partnerships and cooperations
10.1 International initiatives
10.1.1 Visits to international teams
Research stays abroad
Olivier Simonin visited the University of Sherbrooke and the 3IT Institute (Institut interdisciplinaire d'innovation technologique), Canada, in September 2022 (one week). During this short visit, he met Prof. François Michaud and his lab (IntRoLab Laboratoire de robotique intelligente / interactive / intégrée / interdisciplinaire). They worked to the preparation of a collaboration between their teams and to the visit of Prof. Michaud in Lyon Center in 2023 (during his sabbatical program).
10.2 European initiatives
10.2.1 H2020 projects
BugWright2 - H2020 ICT
(Autonomous Robotic Inspection and Maintenance on Ship Hulls and Storage Tanks)
- 650€ for Chroma and Agora teams - total 10 M€ — 2020-24
- The project deals with the inspection of large infrastructures conducted by multiple heterogeneous robots (aerial, ground and underwater). Chroma coordinates the Work Package 6 on multi-robot planning, led by O. Simonin.
- Consortium (academic partners only): CNRS/GeorgiaTech Metz (coord), INSA-Inria Lyon 5chroma & Agora teams), LakeSide lab. (Austria), Universität Klagenfurt, Universitat Trier, Universidade de Porto, Universitat de Les Illes Balears.
- www.bugwright2.eu/
CPS4EU - H2020 ECSEL
(European Initiative to Enable Validation for Highly Automated Safe and Secure Systems)
- 72 K€ Europe + 101 K€ PSPC for Chroma — Period 2019-2022
- The CPS4EU consortium is composed of 36 members including large groups, medium enterprises, SMEs, Universities and RTOs from 5 countries (France, Germany, Spain, Italy, Hungary)
10.3 National initiatives
10.3.1 ANR
ANR MAMUT (2023-2026)
(Machine learning And Metaheuristics algorithms for Urban Transportation)
Participants: Christine Solnon, Jilles Dibangoye, Olivier Simonin.
Consortium: Lab-STICC (coord.), Chroma/CITI, MapoTempo. The main objective of MAMUT is to develop new algorithms for optimizing urban delivery tours. Total funding 522 K€.
ANR JCJC "AVENUE" (2023-2026)
(Cooperative Aerial Vehicles for Non-Uniform Mapping of 3D Unknown Environments)
Participants: Alessandro Renzaglia.
The objective of AVENUE is to propose new efficient solutions to generate online trajectories for a team of cooperating aerial vehicles to achieve complete exploration and non-uniform mapping of an unknown 3D environment. The main challenges will be the definition of new criteria to predict the expected information gain brought by future candidate observation points and the design of a distributed strategy to optimally assign future viewpoints to the robots to finally minimize the total mission time. Total funding 250K€.
ANR "MaestrIoT" (2021-2025)
(Multi-Agent Trust Decision Process for the Internet of Things)
Participants: Jilles Dibangoye, Olivier Simonin.
Consortium: LITIS (coord.), Chroma/CITI, LCIS, IHF/LIMOS. The main objective of the MaestrIoT project is to develop an algorithmic framework for ensuring trust in a multi-agent system handling sensors and actuators of a cyber-physical environment. Trust management has to be ensured from the perception to decision making and integrating the exchange of information between WoT devices. Total funding 536 K€.
ANR "CONCERTO" (2020-23)
Participants: Olivier Simonin, Alexandre Bonnefond.
Title: "mobilité Contrôlée et cOmmunicatioNs effiCaces dans une flottE de dRones auTo-Organisée". The project is led by Isabelle Guerin-Lassous (LIP/Inria Dante). Partners: LIP (UCBL/Inria Dante), CITI (INSA/Inria Chroma), LS2N (CNRS, Nantes), LORIA (UL, Nancy), Alerion (company in Nancy). Funding: 300K€ - (ASTRID ANR).
ANR "Annapolis" (2022-2026)
Participants: Anne Spalanzani.
Title: "AutoNomous Navigation Among Personal mObiLity devIceS". In ANNAPOLIS, unforeseen and unexpected events take source from situations where the perception space is hidden by bulky road obstacles (e.g. truck/bus) or an occluding environment, from the presence of new powered personal mobility platforms, or from erratic behaviors of unstable pedestrians using (or not) new electrical mobility systems and respecting (or not) the traffic rules ANNAPOLIS will increase the vehicle's perception capacity both in terms of precision, measurement field of view and information semantics, through vehicle to intelligent infrastructure communication. Total funding 831 K€.
EquipEx+ "TIRREX" (2021-30)
Participants: Olivier Simonin, Alessandro Renzaglia, Christian Laugier, Lukas Rummelhard.
Title : "Technological Infrastructure for Robotics Research of Excellence" ( 12M€). TIRREX is led by CNRS and involves 32 laboratories. Chroma is involved in two research axes :- "Aerial Robotics", Chroma/CITI lab. is a major partner of this axis (INSA Lyon & Inria). We can benefit from the experimental platforms (in Grenoble and Marseille) and their support.
- "Autonomous land robotics", Chroma/CITI lab. is a secondary partner of this axis (INSA Lyon & Inria).
AI Chair "REMEMBER" (2020-23) (Chair of research and teaching in artificial intelligence)
Participants: Christian Wolf (NaverLabs europe, LIRIS/INSA Lyon), Olivier Simonin, Jilles Dibangoye.
Title : Learning Reasoning, Memory and Behavior (funding 574K€). This Chair is led by Christian Wolf (INSA Lyon/LIRIS lab.), who recently moved to NaverLabs Europe. It involves CITI/Chroma (O. Simonin, J. Dibangoye) and LIRIS/SyCoSMA (L. Matignon). The chair is co-financed by ANR, Naver Labs Europe and INSA-Lyon. Creating agents capable of high-level reasoning based on structured memory is the main topic of the AI Chair "REMEMBER". Funding one PhD in Chroma (P. Marza).
ANR JCJC "Plasma" (2019-2022)
Participants: Jilles Dibangoye.
The ANR JCJC Plasma, led by Jilles S. Dibangoye, aims at developing a general theory and algorithms with provable guarantees to treat planning and (deep) RL problems arising from the study of multi-agent sequential decision-making, which may be described as Partially Observable Stochastic Games (POSG), see Figure 1. We shall contribute to the development of theoretical foundations of the fields of intelligent agents and MASs by characterizing the underlying structure of the multi-agent decision-making problems and designing scalable and error-bounded algorithms. The research group is made of three senior researchers, O. Simonin, F. Charpillet (INRIA Nancy) and O. Buffet (INRIA Nancy), and two junior researchers Jilles S. Dibangoye and A. Saffidine (Univeristy of New South Whales). We received a support for 42-months starting in March 2020 with a financial support of about 254K euros (one PhD and one post-doc are in progress).
ANR "Delicio" (2019-2022)
Participants: Jilles Dibangoye, Olivier Simonin.
The ANR Delicio (Data and Prior, Machine Learning and Control), led by C. Wolf (NaverLabs Europe/INSA Lyon), proposes fundamental and applied research in the areas of Machine Learning and Control with applications to drone (UAV) fleet control. The consortium is made of 3 academic partners: INSA-Lyon/LIRIS, INSA-Lyon/CITI (Chroma team), University Lyon 1/LAGEPP, and ONERA. We received a support for 48-months starting in October 2019 with a financial support of about 540K euros.
ANR "HIANIC" (2018-22)
Participants: Anne Spalanzani, Manon Predhumeau, Maria Kabtoul.
The HIANIC project, led by A. Spalanzani, proposes to endow autonomous vehicles with smart behaviors (cooperation, negotiation, socially acceptable movements) that better suit complex SharedSpace situations. It will integrate models of human behaviors (pedestrian, crowds and passengers), social rules, as well as smart navigation strategies that will manage interdependent behaviors of road users and of cybercars. The consortium is made of 3 academic partners: Inria (RITS, Chroma, Pervasive Interaction teams), LIG Laboratory (Hawai team) and LS2N laboratory (ARMEN and PACCE teams).10.3.2 PEPR
PEPR Agroécologie et numérique: NINSAR project
(New ItiNerarieS for Agroecology using cooperative Robots, 60 months, since 1/1/2023).
Participants: Olivier Simonin, Alessandro Renzaglia, Jilles Dibangoye.
Chroma is partner of the NINSAR project. The project will fund a PhD thesis on heterogenous ground & aerial robot cooperation and path-planning. Olivier Simonin coordinates our participation (168 K€ for Chroma partner, the total funding is 2,16 M€)
PEPR O2R Organic Robotics
. (96 months, since 1/1/2023)
Participants: Olivier Simonin, Anne Spalanzani, Alessandro Renzaglia, Jacques Saraydaryan.
Chroma is involved in the O2R's project "Interactive Mobile Manipulation" (led by Andrea Cherubini from Université de Montpellier/LIRMM). Budget 3.5 M€.
Main topics adressed by Chroma are Social navigation, Multi-robot planning & NAMO problems and Perception of complex scenes with humans.
10.3.3 Grand Defis
Grand Défi "PRISSMA" (2021-2024)
Participants: Alessandro Renzaglia, Christian Laugier, Jean-Baptiste Horel, Pierrick Koch.
The project is funding 330K€ for Chroma (6.5M€ total). The PRISSMA consortium is composed of 21 French members from both industry and academia, including: UTAC (coord.), Inria (Chroma, Convecs), LNE, UGE, CEA, Navya, IRT SystemX, and others. This project aims at proposing a platform that will allow to lift the technological barriers preventing the deployment of secure AI-based systems, and to integrate all the elements necessary for the realization of the homologation activities of the autonomous vehicle and its validation in its environment for a given use case.
10.3.4 FUI Projects
FUI STAR (2018 – 2022)
Participants: Andres Gomez Hernandez, Olivier Simonin, Christian Laugier.
The Project STAR is coordinated by IVECO. The academic partners of the project are Inria Grenoble-Rhône-Alpes, IFSTTAR, ISAE-Supaéro. The industrial and application partners are IVECO, Easymile, Transpolis, Transdev and Sector Groupe. The goal of the project is to build an autonomous bus that will operate on a safe lane Inria is involved in helping design situation awareness perception, especialy in special case like docking at the bus stop and handling dynamicity of any obstacle. The IRT Nanoelec is also involved in the project as a subcontractor, for testing the perception, decision-making, navigation and controls components developed in the project.10.3.5 DGA/INRIA AI projects
"DYNAFLOCK" (2019-2023)
Participants: Alexandre Bonnefond, Olivier Simonin, Isabelle Guerin-Lassous (Lip/Lyon 1, Inria Dante), Johan Faure.
The DYNAFLOCK project, led by O. Simonin, aims to extend flocking-based decentralized control of swarm of UAVs by considering the link quality between communicating entities. The consortium is made of 2 Inria teams from Lyon : Chroma and Dante (involving Prof. I. Guerin-Lassous). The PhD student (Alexandre Bonnefond) recruited in this project aims at defining dynamic flocking models based on the link quality (54). In 2022, Johan Faure has been recruited as engineer to develop simulations and to conduct experiments with a quadrotors platform.
Funding of Dynaflock : 250 K€
10.4 Regional initiatives
Region-funded R&D Booster "Moov-IT" project (2020 – 2023)
Participants: Amrita Suresh, Thomas Genevois, Christian Laugier.
The objective of the project is to develop an autonomous system to be integrated in production chains to provide modernization, flexibility and productivity, including fixed and mobile transitic systems. In that perspective, Chroma's CMCDOT framework will be adapted, extended and integrated on a mobile robot from Akeoplus, and tested in real environments.
FIL (Lyon) Project (2022 – 2023)
(Learning for robotic navigation among humans: toward adaptive paths in dynamic environment)
Participants: Jacques Saraydaryan, Laetitia Matignon (LIRIS), Olivier Simonin.
Transversal Project FIL (Fédération d'informatique de Lyon), 6 600 € for 2 years (2 Master students)
Objectives : Robot navigation among human and dynamic environment belong to complex multifactor problems. Some recent approaches use Deep Learning methods associated to reinforcement learning to deal with such complexity. The project intends to extends such approach to introduce more realistic constraints and to include multi-robot navigation strategies.
2022 : The project funded the Master thesis of Yohan Michelland, intitled "Apprentissage pour la navigation robotique parmi les humains : vers des chemins s’adaptant aux dynamiques de l’environnement".
FIL (Lyon) Project (2023 – 2024)
(CROSS : Safe Navigation of Autonomous Vehicles in Dense Pedestrian Crowds : Learning to Cross)
Participants: Olivier Simonin, Alexandre Nicolas (ILM/CNRS).
Transversal Project FIL (Fédération d'informatique de Lyon), 6 600 € for 2 years (2 Master students)
Objectives : Navigation through dense crowds has recently started to attract academic interest, but these endeavours are faced with the intricacy of modelling the response of such crowds. Project CROSS is aimed at unlocking this situation by modelling admissible and non-admissible trajectories of a (simplified) autonomous car through a crowd. More precisely, agent-based models will be exploited and further developed to simulate a realistic crowd’s response to the traversing motion of an autonomous vehicle, by combining both physics and AI models.
A first master will start in march 2023 on "Crowds' response to their crossing by an autonomous vehicle".
11 Dissemination
Participants: all members .
11.1 Promoting scientific activities
11.1.1 Scientific events: organisation
- Christine Solnon co-organized the ROADEF 2022 conference (23ème édition du congrès annuel de la Société Française de Recherche Opérationnelle et d'Aide à la Décision) which welcomed 570 participants at INSA Lyon, 23-25 fev. roadef2022.sciencesconf.org/
- Christian Laugier co-organized a half-day Special Session at the conference IEEE ICARCV 2022 (Singapore, December 2022). Title of the session: Outdoor autonomous systems: theory, technology and applications. Co-organizers: Danwei Wang, Christian Laugier and Philippe Martinet.
- Christian Laugier co-organized two workshops at the IEEE/RSJ IROS 2022 (Kyoto, October 2022) conference: The PPNIV 2022 workshop (about 250 on-site attendees + several remote attendees) and the PNARUDE 2022 workshop (on-site and remote attendees).
- Christian Laugier was member of the Organizing Committee and Chair of the keynote session on “Future Autonomous Systems” of the IROS@35 Forum. This forum was held in the scope of the IEEE/RSJ IROS 2022 conference (Kyoto, October 2022).
- Olivier Simonin was member of the organization and program committee of the "Journées Scientifique Inria 2022", organized at Inria Rocquencourt (23-25 nov. 2022) jsi2022.inria.fr/.
11.1.2 Scientific events: selection
Chair of conference program committees
- Christian Laugier was appointed Editor-in-Chief of the IROS Conference Paper Review Board (CPRB) for the period 2023-25 (IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems).
- Christine Solnon was program chair of the 28th International Conference on Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming (CP 2022) 37, which was part of the Federated Logic Conference (FLoC).
Member of the conference program committees
- Christian Laugier was Senior Editor for IROS 2022 (IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems).
- Christian Laugier was Associate Editor for ICRA 2022 (IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation).
- Christian Laugier was Associate Editor for IV 2022 (IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium).
- Christine Solnon was member of the program committees of CP-AI-OR 2022, IJCAI-ECAI 2022 (top 3% reviewer), and AAAI 2022.
- Olivier Simonin was member of the program committees of IJCAI-ECAI 2022, DARS 2022 (The 16th International Symposium on Distributed Autonomous Robotic Systems 2022), CNIA 2002 (Conférence Nationale en Intelligence Artificielle) and JFSMA 2022 (30èmes Journées Francophones sur les Systèmes Multi-Agents).
- Alessandro Renzaglia was Associate Editor for IROS 2022 (IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems) and program committee member for DARS 2022 (16th International Symposium on Distributed Autonomous Robotic Systems).
- Agostino Martinelli was Associate Editor for ICRA 2022 (IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation).
- David Sierra-Gonzalez was Associate Editor for IROS 2022 (IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems).
- Jilles Dibangoye was senior program committee member of AAAI 2022, International Conference on Artificial Intelligence.
Reviewer
- O. Simonin, A. Martinelli, C. Laugier, A. Spalanzani and A. Renzaglia serve each year as reviewer in conferences ICRA and IROS.
11.1.3 Journal
Member of the editorial boards
- Christine Solnon is associate editor of Annals of Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence (AMAI), and member of the editorial boards of Swarm Intelligence, and Constraints.
- Olivier Simonin is a member of the editorial board of the french revue of AI since 2018, named RIA till 2020 and ROIA now.
- C. Laugier is member of the Editorial Board of the journal IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles (Senior Editor). He is also member of the Steering Committee of the Journal.
- C. Laugier is member of the Editorial Board of the IEEE Journal Robomech.
Reviewer - reviewing activities
- O. Simonin was reviewer for RA-L Journal (IEEE Robotics and Automation Letter) and ROIA (Revue Ouverte d'Intelligence Française).
11.1.4 Invited talks
- Christine Solnon gave an invited talk at ROADEF'22 on "Should we take into account traffic conditions when solving routing problems?"
- Olivier Simonin gave an invited talk at the 3IT institute from Sherbrooke University, Canada "Coordination multi-robot en environments dynamiques et contraints" (Sept. 28th 2022).
- Anne Spalanzani gave an invited talk at the international symposium "human at the center of HRI" co-organized by Naverlab and Inria.
- Anne Spalanzani gave an invited talk at the PPNIV Workshop (on autonomous vehicles) of the IROS'22 conference.
- Christian Laugier gave an invited talk at JTR 2022 titled "Véhicule Autonomes dans un contexte de Trafic Mixte- Enjeux, Technologies et Verrous Scientifiques" (Nantes, 10-11 May 2022).
11.1.5 Leadership within the scientific community
- Christine Solnon is member of the "comité de direction" of the GDR IA (www.gdria.fr)
- Christine Solnon is member of the "Conseil d'Administration" of the TUBA (lyonurbandata.sfr-monsitebusiness.fr)
- Olivier Simonin is member of the Executive Committee of the PEPR O2R (Organic Robotics) 2023-2030 (www.cnrs.fr/en/pepr/pepr-exploratoire-o2r-robotique).
- Olivier Simonin and Fabrice Jumel are members of Robocup France committee: (www.robocup.fr/le-comite)
- Fabrice Jumel is a member of the organization committee of the Robocup@Home competition (since 2016).
- Christian Laugier is a founding member and co-chair of the IEEE RAS Technical Committee on "Autonomous Ground Vehicles and Intelligent Transportation Systems"
- David Sierra-Gonzalez is a junior co-chair of the IEEE RAS Technical Committee on "Autonomous Ground Vehicles and Intelligent Transportation Systems"
11.1.6 Scientific expertise
- Anne Spalanzani was expert for evaluation of the Einstein Center project on urban mobility (Berlin).
- Olivier Simonin was a member of the committee of the ANR CE33 call (Interaction, Robotique) in 2022.
- Olivier Simonin was expert in the evaluation committee of the 3IT institute from University of Sherbrooke, Canada (Sept. 2022).
11.1.7 Research administration
- O. Simonin is member of the Inria Lyon COS (comité d'orientation scientifique du Centre).
11.2 Teaching - Supervision - Juries
11.2.1 Supervision
Phd in progress :
- Rabbia Asghar, Real-time analysis of complex traffic situations by Predicting/Characterizing Abnormal Behaviors and Dangerous Situations, A. Spalanzani, C. Lauguier.
- Manuel Diaz Zapata, AI-based Framework for Scene Understanding and Situation Awareness for Autonomous Vehicles, J. Dibangoye, C. Laugier, O. Simonin.
- Benoit Renault, Navigation coopérative et sociale de robots mobiles en environnement modifiable, O. Simonin and J. Saraydaryan.
- Jean-Baptiste Horel, Validation des composants de perception basés sur l’IA dans les véhicules autonomes, R. Mateescu (Inria Convecs), A. Renzaglia, C. Laugier, funded by PRISSMA project.
- Luiz Serafim-Guardini, Conduite Automobile Autonome : Utilisation de grilles d'occupation probabilistes dynamiques pour la planification contextualisée de trajectoire d'urgence à criticité minimale, A. Spalanzani, C. Laugier, P. Martinet (Inria acentauri).
- Alexandre Bonnefond, Large-scale automatic learning of autonomous agent behavior with structured deep reinforcement learning, O. Simonin and I. Guerrin-Lassous (Inria Dante).
- Mihai Popescu, Planification multi-agents pour la patrouille d'un réseau de cibles découvertes dynamiquement, O. Simonin, A. Spalanzani, F. Valois (CITI/Inria Agora) (on break in 2020).
- Estéban Carvalho, Safe and aggressive piloting of UAVs, 2019, Ahmad Hably (Gipsa-Lab), Nicolas Marchand (Gipsa-Lab), Jilles S. Dibangoye.
- Xiao Peng, Planification sous contraintes d’une flotte de robots mobiles pour des tâches de couverture spatiale, O. Simonin, C. Solnon, European H2020 BugWright2 project funding.
- Pierre Marza, Apprentissage large-échelle d'agents autonomes capables de naviguer dans des environnements réels, C. Wolf, L. Matignon, O. Simonin, funded by Chaire IA "REMEMBER".
- Aurelien Delage, Zero-Sum Partially Observable Stochastic Games, Jilles Dibangoye and Olivier Buffet (Larsen Inria), funded by ANR JCJC PLASMA.
- Zoboli Samuel, Learning globalization of locally stabilizable policies for nonlinear systems, Jilles Dibangoye, Vincent Andrieu and Daniele Astolfi (LAGEPP,Lyon), funded by ANR PRC Delicio.
- Romain Fontaine, Optimisation de la mobilité en ville en tenant compte des conditions de traffic, J. Dibangoye and C. Solnon.
- Léon Fauste, Aide à la décision pour le choix de l'échelle lors de la relocalisation d'activités industrielles, M. Mangeot (STEEP, Inria Montbonnot), J.-Y. Courtonne (STEEP, Inria Montbonnot), and C. Solnon.
Phd defended in 2022 :
- Edward Beeching, Large-scale automatic learning of autonomous agent behavior with structured deep reinforcement learning, C. Wolf, O. Simonin and J. Dibangoye.
- Loic Rouquette, Programmation par contraintes pour la cryptanalyse symétrique, M. Minier (LORIA) and C. Solnon.
11.2.2 Juries
- Christine Solnon was president of the PhD thesis jury of Gregory Martin (Rennes), Adrien Varet (Marseille), Sami Mohamed Cherif (Marseille), Rémi Viola (Saint Etienne), Anna Takayasu (Lyon), and Loïc Bonnetain (Lyon);
- Christine Solnon was member of the PhD theses jury of Ryma Boumazouza (Lens), Arnold Hien (Caen), Loïc Rouquette (Lyon), Edward Beeching (Lyon), Léa Blaise (Toulouse), Fulya Trosser (Toulouse)
- Anne Spalanzani was member of the PhD these jury of Andrei Mitriakov (Brest), Julien Uzzan (Nancy), Phani-Teja Singamaneni (Toulouse) and Renaud Poncelet (Paris).
- Olivier Simonin was president of the HDR jury of Christophe Lang (Besançon, FEMTO).
- Olivier Simonin was president of the PhD thesis jury of Guilhem Marcillaud (Toulouse, IRIT).
- Olivier Simonin was member, as reviewer, of the PhD these jury of Antoine Milot (Toulouse, LAAS/ONERA) and Zheng Ze Zhu (Clermont-Ferrand, LIMOS/Institut Pascal).
- Olivier Simonin was member of the PhD these jury of Daravuth Koung (Nantes, LS2N).
11.3 Popularization
11.3.1 Articles and contents
- Christine Solnon has written a chronicle on the last volume of the art of computer programming in "La Recherche" 45 (www.larecherche.fr/lart-d'écrire-des-programmes)
- Anne Spalanzani was interviewed for the Journal Data Analytics Post « Pour la voiture totalement autonome, les chercheurs demandent… un petit délai ;-) »
- Anne spalanzani was interviewed for the Journal Inria National "les vehicules autonomes sont-ils vraiment pour demain ?"
- Fabrice Jumel gave a talk to the Master students from UCLY (Lyon) "Intelligence Artificielle et Ethique".
11.3.2 Education
Olivier Simonin:
- INSA Lyon 5th year / Master - Robotics option (20 students) : AI for Robotics, Multi-Robot Systems, Robotics Projects, 80h, Resp., Telecom Dept.
- INSA Lyon 4th year / Master. : Introduction to AI, 10h (90 students), Telecom Dept.
- INSA Lyon 3rd year / Lic. : Algorithmics, 50h (90 students), L3, Resp., Telecom Dept.
Jilles S. Dibangoye :
- INSA Lyon 4th year / Master : Introduction to AI, 20h (90 students), Resp., Telecom Dept.
- INSA Lyon 3rd year / Lic. : Algorithmics, 32h, Telecom Dept.
- INSA Lyon 3rd year / Lic. & Master : Operating Systems, 56h L3 and 16h Master, Telecom Dept.
- INSA Lyon 5th year / Master : AI for Robotics 18h, Telecom Dept.
Christine Solnon :
- INSA Lyon 3rd year / Lic. : Advanced algorithms for artificial intelligence and graphs, 40h (130 students), Resp., Computer Science Dept.
- INSA Lyon 4th year / Master : Object Oriented and Agile software development, 62h (130 students), Resp., Computer Science Dept.
- INSA Lyon 5th year / Master : Fundamental Computer Science, 20h (60 students), Resp., Computer Science Dept.
- INSA Lyon 5th year / Master : Prescriptive Data Analytics, 6h (30 students), Computer Science Dept.
Fabrice Jumel :
- CPE Lyon 4-5th year / Master : Robotics option, 400h, Resp., SN Dept.
- CPE Lyon 4-5th year / Master : Robotic vision, cognitive science, HRI, deeplearning, robotic platforms, Kalman Filter, 250h., SN Dept.
Jacques Saraydaryan :
- CPE Lyon 5th year / Master : Autonomous Robot Navigation 18h, Particle Filter 12h, Robotics Middleware 16h, SN Dept.
- CPE Lyon 4-5th year / Master : Software Design and Big Data, 400h, Resp., SN Dept.
- CPE Lyon 4-5th year / Master : Software Architecture, 140h, SN Dept.
- CPE Lyon 4-5th year / Master : Introduction to Cyber Security, 48h, SN Dept.
Anne Spalanzani :
- INPG Ense3 Grenoble, Master MARS: Autonomous Robot Navigation 9h.
Agostino Martinelli:
- Master (M2R) MoSIG: Autonomous Robotics, 12h, ENSIMAG Grenoble.
Alessandro Renzaglia:
- INPG Ense3 Grenoble, Master MARS: AI and Autonomous Systems, 4h.
- INSA Lyon 5th year / Master - Robotics option: Multi-Robot Systems, 2h, Telecom Dept.
- INSA Lyon 3rd year / Lic.: supervision of research initiation projects (groups of 5 students) along one semester, 15h, Telecom Dept.
11.3.3 Interventions
- Fabrice Jumel coordinated the Mobile Robotic area of the national WorldSkills event in Eurexpo (Lyon), January 13-15 2022.
12 Scientific production
12.1 Major publications
- 1 articleSolving Multi-Agent Routing Problems Using Deep Attention Mechanisms.IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation SystemsJuly 2021, 1-10
- 2 incollectionHandbook of Robotics 2nd edition, Chapter 62 on ''Intelligent Vehicles''.Handbook of Robotics 2nd EditionSpringer VerlagJuly 2016
- 3 inproceedingsSemantic Grid Estimation with a Hybrid Bayesian and Deep Neural Network Approach.IROS 2018 - IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and SystemsMadrid, SpainIEEEOctober 2018, 1-8
- 4 inproceedingsTowards Proactive Navigation: A Pedestrian-Vehicle Cooperation Based Behavioral Model.2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation ProceedingsParis, FranceMay 2020, 6958-6964
- 5 articleCooperative Visual-Inertial Odometry: Analysis of Singularities, Degeneracies and Minimal Cases.IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters522020, 668 - 675
- 6 articleNonlinear Unknown Input Observability: Extension of the Observability Rank Condition.IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control641January 2019, 222 - 237
- 7 inproceedingsSolving the Non-Crossing MAPF with CP.CP 2021 - 27th International Conference on Principles and Practice of Constraint ProgrammingLIPIcs: Leibniz International Proceedings in InformaticsMontpellier (on line), FranceOctober 2021, 1-17
- 8 inproceedingsAn Agent-Based Model to Predict Pedestrians Trajectories with an Autonomous Vehicle in Shared Spaces.Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS 2021)AAMAS 2021 - 20th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent SystemsOnline, FranceMay 2021, 1-9
- 9 articleA Common Optimization Framework for Multi-Robot Exploration and Coverage in 3D Environments.Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems2020
- 10 inproceedingsReinforcement Learning Policies With Local LQR Guarantees For Nonlinear Discrete-Time Systems.2021 60th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC)CDC 2021 - 60th IEEE Conference on Decision and ControlTexas, United StatesIEEEDecember 2021
12.2 Publications of the year
International journals
International peer-reviewed conferences
National peer-reviewed Conferences
Edition (books, proceedings, special issue of a journal)
Doctoral dissertations and habilitation theses
Reports & preprints
Other scientific publications
12.3 Other
Scientific popularization
12.4 Cited publications
- 46 inproceedingsVehicle Localization Based on Visual Lane Marking and Topological Map Matching.ICRA 2020 - IEEE International Conference on Robotics and AutomationParis, FranceIEEEMay 2020, 258-264
- 47 phdthesisCrossing of Road Intersections: Decision-Making Under Uncertainty for Autonomous Vehicles.Comue Université Grenoble AlpesDecember 2019
- 48 incollectionValidation Framework Applied to the Decision-Making Process for an Autonomous Vehicle Crossing Road Intersections.Validation and Verification of Automated SystemsSpringer International PublishingNovember 2020, 179-205
- 49 inproceedingsValidation of Perception and Decision-Making Systems for Autonomous Driving via Statistical Model Checking.IV 2019 - 30th IEEE Intelligent Vehicles SymposiumParis, FranceIEEEJune 2019, 252-259
- 50 inproceedingsEgoMap: Projective mapping and structured egocentric memory for Deep RL.ECML-PKDD 2020 - European Conference on Machine Learning and Principles and Practice of Knowledge Discovery in Databaseshttps://arxiv.org/abs/2002.02286ghent, BelgiumSeptember 2020, 1-12
- 51 inproceedingsLearning to plan with uncertain topological maps.ECCV 2020 - 16th European Conference on Computer VisionGlasgow, United KingdomAugust 2020, 1-24
- 52 inproceedingsDeep Reinforcement Learning on a Budget: 3D Control and Reasoning Without a Supercomputer.ICPR 2020 - 25th International Conference on Pattern RecognitionMilan, ItalyDecember 2020, 1-16
- 53 bookDynamic Programming.Dover Publications, Incorporated1957
- 54 inproceedingsExtension of Flocking Models to Environments with Obstacles and Degraded Communications.IROS 2021 - IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and SystemsProceedings IROS 2021Prague / Virtual, Czech RepublicIEEESeptember 2021, 9139-9145
- 55 phdthesisDeep multi-agent reinforcement learning for dynamic and stochastic vehicle routing problems.Université de LyonOctober 2020
- 56 articleMulti-Robot Symmetric Formations for Gradient and Hessian Estimation with Application to Source Seeking.IEEE Transactions on Robotics353June 2019, 782-789
- 57 unpublishedOn Bellman's Optimality Principle for zs-POSGs.December 2020, https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.16395v1 - working paper or preprint
- 58 inproceedingsSur le principe d'optimalité de Bellman pour les zs-POSG.JFPDA 2020 - Journées Francophones surla Planification, la Décision et l’Apprentissagepour la conduite de systèmesAngers (virtuel), FranceJune 2020, 1-3
- 59 articleHeuristic Search Value Iteration for zero-sum Stochastic Games.IEEE Transactions on Games1332021, 1-10
- 60 inproceedingsTowards semantic SLAM using a monocular camera.IROS2011
- 61 unpublishedHSVI fo zs-POSGs using Concavity, Convexity and Lipschitz Properties.October 2021, 37 pages, 4 figures, 4 tables, 3 algorithms
- 62 inproceedingsInstance Segmentation with Unsupervised Adaptation to Different Domains for Autonomous Vehicles.ICARCV 2020 - 16th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and VisionShenzen, ChinaDecember 2020, 1-7
- 63 articleOptimally Solving Dec-POMDPs as Continuous-State MDPs.Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research55February 2016, 443-497
- 64 inproceedingsLearning to Act in Decentralized Partially Observable MDPs.ICML 2018 - 35th International Conference on Machine Learning80Proceedings of Machine Learning ResearchStockholm, SwedenPMLR2018, 1233-1242
- 65 articleSemantic Segmentation with Unsupervised Domain Adaptation Under Varying Weather Conditions for Autonomous Vehicles.IEEE Robotics and Automation LettersMarch 2020, 1-8
- 66 inproceedingsGridTrack: Detection and Tracking of Multiple Objects in Dynamic Occupancy Grids.ICVS 2021 - International Conference on Vision SystemsVirtual Conference, AustriaOctober 2021, 1-14
- 67 articleEnd-to-End Learning of Semantic Grid Estimation Deep Neural Network with Occupancy Grids.Unmanned systems73July 2019, 171-181
- 68 inproceedingsSemantic Grid Estimation with Occupancy Grids and Semantic Segmentation Networks.ICARCV 2018 - 15th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and VisionSingapore, SingaporeNovember 2018, 1-6
- 69 inproceedingsSemantic Grid Estimation with a Hybrid Bayesian and Deep Neural Network Approach.IROS 2018 - IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and SystemsMadrid, SpainIEEEOctober 2018, 1-8
-
70
inproceedings
-POMDPs have Lipschitz-Continuous -Optimal Value Functions.NIPS 2018 - Thirty-second Conference on Neural Information Processing SystemsMontréal, CanadaDecember 2018 - 71 inproceedingsApproche hybride de résolution pour le Time-Dependent Traveling Salesman Problem with Time Windows.23ème congrès annuel de la Société Française de Recherche Opérationnelle et d'Aide à la DécisionINSA LyonVilleurbanne - Lyon, FranceFebruary 2022
- 72 articleVerifying Collision Risk Estimation using Autonomous Driving Scenarios Derived from a Formal Model.Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems2023
- 73 inproceedingsContext Aware Robot Architecture, Application to the RoboCup@Home Challenge.RoboCup symposiumMontreal, CanadaJune 2018, 1-12
- 74 inproceedingsMapping likelihood of encountering humans: application to path planning in crowded environment.The European Conference on Mobile Robotics (ECMR)Proceedings of ECMR 2017Paris, FranceSeptember 2017
- 75 inproceedingsProactive Longitudinal Velocity Control In Pedestrians-Vehicle Interaction Scenarios.ITSC 2020 - 23rd IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation SystemsRhodes, GreeceIEEESeptember 2020, 1-6
- 76 inproceedingsTowards Proactive Navigation: A Pedestrian-Vehicle Cooperation Based Behavioral Model.ICRA 2020 - IEEE International Conference on Robotics and AutomationIEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation ProceedingsParis, FranceMay 2020, 6958-6964
- 77 articleDARP: divide areas algorithm for optimal multi-robot coverage path planning.Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems8632017, 663--680
- 78 bookPlanning Algorithms.Available at http://planning.cs.uiuc.edu/Cambridge, U.K.Cambridge University Press2006
- 79 articleAutomatic Search of Rectangle Attacks on Feistel Ciphers: Application to WARP.IACR Transactions on Symmetric Cryptology20222June 2022, 113-140
- 80 inproceedingsA journey in the history of Automated Driving.IROS 2019 - IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and SystemsInvited Pionneer's talk at IEEE/RSJ IROS 2019Macau, ChinaIEEENovember 2019, 1-27
- 81 techreportBayesian & AI driven Embedded Perception and Decision-making. Application to Autonomous Navigation in Complex, Dynamic, Uncertain and Human-populated Environments.Synoptic of Research Activity, Period 2004-20 and beyond.INRIA Grenoble - Rhone-Alpes ; LIG (Laboratoire informatique de Grenoble)February 2021
- 82 inproceedingsCombining Bayesian and AI approaches for Autonomous Driving.IROS 2021 - IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems - Workshop ''Perception and Navigation for Autonomous Robotics in Unstructured and Dynamic Environments''Prague, Czech RepublicIEEESeptember 2021
- 83 inproceedingsDynamic Traffic Scene Understanding using Bayesian Sensor Fusion and Motion Prediction.ECCV 2018 - Workshop on Vision-based Navigation for Autonomous DrivingMunich, GermanySeptember 2018, 1-35
- 84 inproceedingsImpact of AI on Autonomous Driving.WRC 2019 - WRC 2019- IEEE World Robot ConferenceBeijing, ChinaIEEEAugust 2019, 1-27
- 85 inproceedingsThe challenge of on-board Perception and Decision-making for Autonomous Driving in Mixed traffic conditions.IROS 2021 - IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems - Interactive session on ''Future advances and research directions for autonomous robotics''Prague, Czech RepublicIEEESeptember 2021
- 86 inproceedingsFormal Validation of Probabilistic Collision Risk Estimation for Autonomous Driving.CIS-RAM 2019 - 9th IEEE International Conference on Cybernetics and Intelligent Systems (CIS) Robotics, Automation and Mechatronics (RAM)Bangkok, ThailandIEEENovember 2019, 1-6
- 87 inproceedingsAutomatic Generation of Declarative Models for Differential Cryptanalysis.CP 2021 - 27th International Conference on Principles and Practice of Constraint ProgrammingLIPIcs--Leibniz International Proceedings in InformaticsMontpellier, FranceOctober 2021
- 88 articleNonlinear Unknown Input Observability and Unknown Input Reconstruction: The General Analytical Solution.arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.076102022
- 89 bookObservability: A New Theory Based on the Group of Invariance.Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics - SIAMJune 2020, 1-259
- 90 inproceedingsMulti-Robot Simultaneous Coverage and Mapping of Complex Scene - Comparison of Different Strategies.AAMAS 2018 - 17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems - Robotics TrackStockholm, SwedenACMJuly 2018, 559-567
- 91 articleFlocking for multi-agent dynamic systems: algorithms and theory.IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control5132006, 401-420
- 92 inproceedingsSolving the Non-Crossing MAPF for non point-sized robots.23ème congrès annuel de la Société Française de Recherche Opérationnelle et d'Aide à la DécisionINSA LyonVilleurbanne - Lyon, FranceFebruary 2022
- 93 inproceedingsProbabilistic Collision Risk Estimation for Autonomous Driving: Validation via Statistical Model Checking.IV 2020 -- 31st IEEE Intelligent Vehicles SymposiumLas Vegas, NV, United StatesOctober 2020, 1-7
- 94 inproceedingsGndNet: Fast Ground Plane Estimation and Point Cloud Segmentation for Autonomous Vehicles.IROS 2020 - IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and SystemsLas Vegas, NV, United StatesIEEEOctober 2020, 2150-2156
- 95 inproceedingsAttentional PointNet for 3D-Object Detection in Point Clouds.CVPR 2019 - Workshop on Autonomous drivingLong Beach, California, United StatesJune 2019, 1-10
- 96 inproceedingsFrustum-PointPillars: A Multi-Stage Approach for 3D Object Detection using RGB Camera and LiDAR.ICCVW 2021 - IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops2nd Autonomous Vehicle Vision (AVVision) Workshop - ICCV 2021California, United StatesOctober 2021, 1-9
- 97 inproceedingsSolving the Non-Crossing MAPF with CP.CP 2021 - 27th International Conference on Principles and Practice of Constraint ProgrammingLIPIcs: Leibniz International Proceedings in InformaticsMontpellier (on line), FranceOctober 2021, 1-17
- 98 inproceedingsAdapting the Social Force Model for Low Density Crowds in Open Environments.15th Social Simulation ConferenceMainz, GermanySeptember 2019
- 99 inproceedingsModeling and Simulating Pedestrian Social Group Behavior with Heterogeneous Social Relationships.SCS 2020 - Spring Simulation ConferenceVirtual event, United StatesMay 2020
- 100 inproceedingsAn Agent-Based Model to Predict Pedestrians Trajectories with an Autonomous Vehicle in Shared Spaces.AAMAS 2021 - 20th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent SystemsInternational Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems (IFAAMAS)Online, FranceMay 2021, 1-9
- 101 articlePedestrian Behavior in Shared Spaces with Autonomous Vehicles: An Integrated Framework and Review.IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles812021, 438-457
- 102 inproceedingsModeling a Social Placement Cost to Extend Navigation Among Movable Obstacles (NAMO) Algorithms.IROS 2020 - IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and SystemsDOI is not yet properly functionnal, go to IEEEXplore directly : https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9340892Las Vegas, United StatesOct 2020, 11345-11351
- 103 articleSearch and Localization of a Weak Source with a Multi-Robot Formation.Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems9732020, 623-634
- 104 articleA Common Optimization Framework for Multi-Robot Exploration and Coverage in 3D Environments.Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems2020
- 105 inproceedingsCombining Stochastic Optimization and Frontiers for Aerial Multi-Robot Exploration of 3D Terrains.IROS 2019 - IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and SystemsMacau, ChinaNovember 2019
- 106 inproceedingsAn asymptotic approximation of the traveling salesman problem with uniform non-overlapping time windows.CASE 2021 - IEEE 17th International Conference on Automation Science and EngineeringLyon, FranceIEEEAugust 2021, 1-6
- 107 inproceedingsabstractXOR: A global constraint dedicated to differential cryptanalysis.26th International Conference on Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming12333LNCSLouvain-la-Neuve, BelgiumSpringerSeptember 2020, 566--584
- 108 inproceedingsNavigation in Human Flows : Planning with Adaptive Motion Grid.IROS Workshop CrowdNavParis, FranceOctober 2018
- 109 inproceedingsPeople management framework using a 2D camera for human-robot social interactions.RoboCup 2019 - 23rd Annual RoboCup International SymposiumRobocup 2019: Robot World Cup XXIIISydney, AustraliaJuly 2019, 1-13
- 110 inproceedingsEmploying Severity of Injury to Contextualize Complex Risk Mitigation Scenarios.IV 2020 -- 31st IEEE Intelligent Vehicles SymposiumLas Vegas / Virtual, United StatesIEEEOctober 2020, 1-7
- 111 mastersthesisDomain adaptation for cross-sensor 3D object detection on point-clouds.MA ThesisUniversite Grenoble AlpesAugust 2020
- 112 inproceedingsModeling Driver Behavior From Demonstrations in Dynamic Environments Using Spatiotemporal Lattices.ICRA 2018 - Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and AutomationBrisbane, AustraliaMay 2018, 3384-3390
- 113 inproceedingsHuman-Like Decision-Making for Automated Driving in Highways.ITSC 2019 - 22nd IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation SystemsAuckland, New ZealandOctober 2019, 1-8
- 114 inproceedingsLeveraging Dynamic Occupancy Grids for 3D Object Detection in Point Clouds.ICARCV 2020 - 16th IEEE International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and VisionShenzhen, ChinaIEEEDecember 2020, 1-6
- 115 phdthesisTowards Human-Like Prediction and Decision-Making for Automated Vehicles in Highway Scenarios.Université Grenoble AlpesApril 2019
- 116 inproceedingsCNN-SLAM: Real-time dense monocular SLAM with learned depth prediction.CVPR2017
- 117 articleOptimized flocking of autonomous drones in confined environments.Science Robotics32018, 2470-2476
- 118 inproceedingsBuilding Prior Knowledge: A Markov Based Pedestrian Prediction Model Using Urban Environmental Data.ICARCV 2018 - 15th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and VisionSingapore, SingaporeNovember 2018, 1-12
- 119 bookTheory of Games and Economic Behavior.Princeton University Press1944
- 120 bookTheory of games and economic behavior.Princeton University Press2007
- 121 inproceedingsOptimally Solving Two-Agent Decentralized POMDPs Under One-Sided Information Sharing.ICML 2020 - 37th International Conference on Machine LearningVienne / Virtual, AustriaJuly 2020, 1-10
- 122 inproceedingsDriving Behavior Assessment and Anomaly Detection for Intelligent Vehicles.CIS-RAM 2019 - 9th IEEE International Conference on Cybernetics and Intelligent Systems (CIS) Robotics, Automation and Mechatronics (RAM)Bangkok, ThailandNovember 2019, 1-6
- 123 inproceedingsReinforcement Learning Policies With Local LQR Guarantees For Nonlinear Discrete-Time Systems.CDCTexas, United StatesIEEEDecember 2021
- 124 inproceedingsDemo: In-flight Localisation of Micro-UAVs using Ultra-Wide Band.EWSN 2020 - International Conference on Embedded Wireless Systems and NetworksLyon, FranceACMFebruary 2020

